Climate change, shrinking arable land, and a soaring global population are challenging how we grow food. By 2050, the world’s population will exceed 9 billion, driving an estimated 59–98% increase in food demand. Traditional farming alone struggles to keep up amid water scarcity and unpredictable weather. That’s where vertical farming steps in with a complementary approach to maximize crop production in minimal space, using controlled environments to ensure consistent yields.
But what are vertical farms, and why the buzz about them? Simply put, vertical farming means growing crops in stacked layers under controlled indoor conditions. It’s gaining traction as a sustainable solution to feed cities fresh produce. While the agriculture industry is suffering from multiple challenges, the benefits of vertical farming have revolutionized production with promising results.
In this blog, we’ll discuss those benefits with proven statistics after understanding the core parameters of vertical farming and its obvious need in the current times. Whether you are a farm owner, agricultural entrepreneur, urban grower, and food retailer, vertical farming offers practical solutions to today’s agricultural challenges respective to every domain.
What is Vertical Farming?
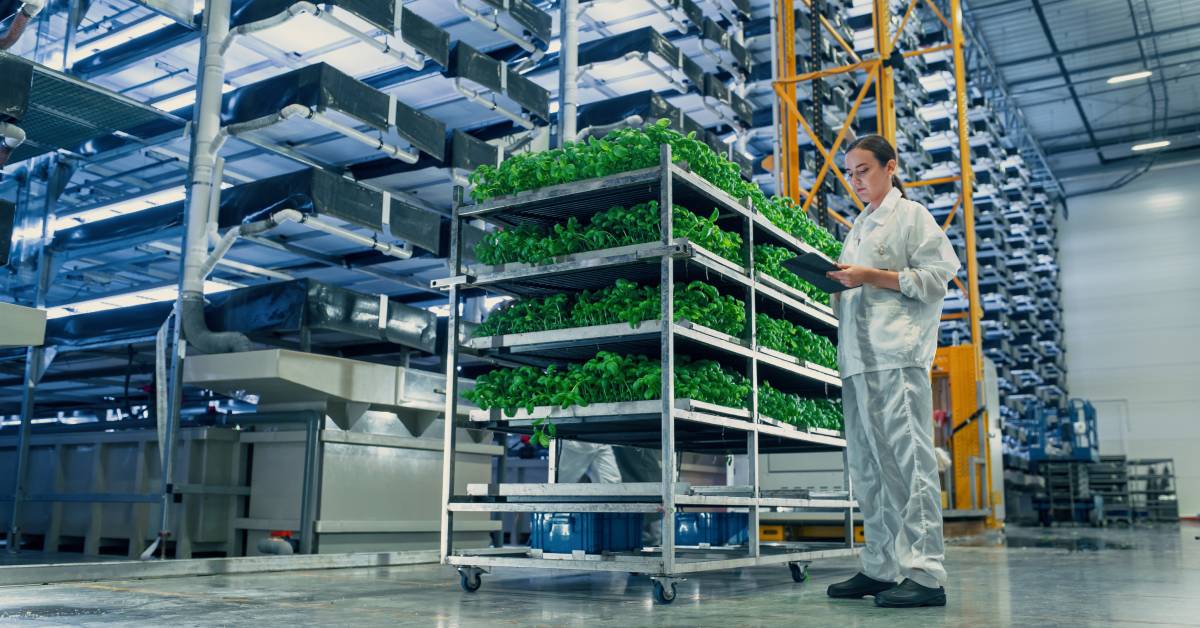
Vertical farming (also known as vertical agriculture farming) is a method of growing plants indoors on vertically stacked shelves or towers, instead of spread out across fields. It’s a form of controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) where factors like light, temperature, and nutrients are precisely regulated.
Instead of soil and sunlight, vertical farms use soilless cultivation systems (hydroponics, aeroponics, or aquaponics) and LED lighting to raise crops in warehouses, greenhouses, or even shipping containers. The result is an artificial farm ecosystem: rows of crops growing under LED lamps, in nutrient-enriched water or mist, all inside a climate-controlled facility.
How Does it Work?
Vertical farms deploy advanced technologies to grow crops efficiently year-round. Key components include dense stacked growing racks, LED lighting tuned to plant needs, and automated climate control for temperature, humidity, and CO₂. Most vertical farms use one of three soilless growing techniques:
- Hydroponics: Plants are grown with their roots in a nutrient-rich water solution instead of soil. The roots sit in or above channels of circulating water that deliver precise nutrients. This hydroponic vertical farm setup feeds plants directly and recycles water, virtually eliminating the runoff and waste seen in field irrigation.
- Aeroponics: Developed by NASA for space missions, aeroponics grows plants with roots suspended in air that are regularly misted with nutrient solution. This innovative aeroponic farming in greenhouses technique uses extremely little water, up to 95% less than even hydroponics, because roots receive ample oxygen. The sterile, mist environment can also boost nutrient uptake, yielding fast growth.
- Aquaponics: This method pairs hydroponic plants with aquaculture technologies in a closed loop. Waste from fish tanks provides organic fertilizer for the plants, and the plants filter and clean the water, which recirculates back to the fish. An aquaponic vertical farm produces both plants and fish together, creating a mini ecosystem that efficiently recycles nutrients.
Why is Vertical Farming Important?
Today, vertical farming is especially relevant given several global challenges. Here are a few key reasons why vertical farming is important now:
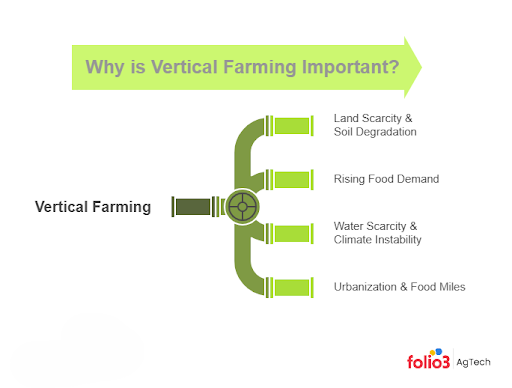
- Land scarcity & soil degradation: A third of the world’s farmable soil has been lost in just 40 years due to erosion and pollution. With fertile land disappearing, vertical farming offers a way to grow food on a minimal footprint without using soil, reducing pressure on the earth’s remaining farmland.
- Rising food demand: The food demand is projected to increase 60–100% over the next two decades. Traditional farming alone may struggle to meet this need. Vertical farming supplements food supply by stacking crops upward, ensuring reliable access to fruits and vegetables.
- Water scarcity & climate instability: Agriculture consumes about 70% of global freshwater. With droughts and extreme weather threatening yields, vertical farms recycle water and maintain steady production year-round. Climate-controlled systems protect crops from floods, frost, or heat waves.
- Urbanization & food miles: Over half the global population now lives in cities, often far from farms. Produce typically travels thousands of miles, losing freshness and adding emissions. Vertical farms can be built within or near cities, providing fresher food, cutting transport costs, and reducing waste.
These drivers have created an urgent need for solutions like vertical farming. That’s why the vertical farming benefits of high farm efficiency, climate resilience, and local production align perfectly with today’s food security needs.
Top 10 Benefits of Vertical Farming
What are the benefits of vertical farming? Below, we break down the advantages of indoor vertical farming, from yield and resource use to community impacts. Each benefit shows what vertical farms can do that traditional farms often cannot:
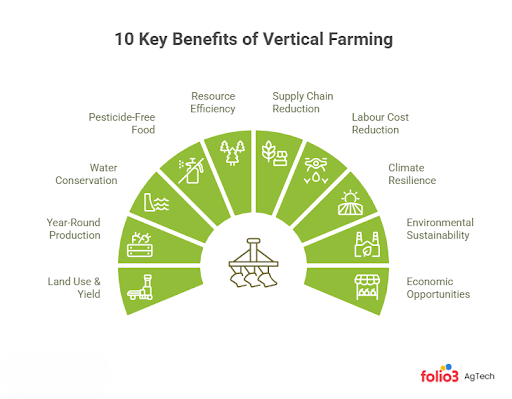
1. Maximizes Land Use & Crop Yield
A key advantage of vertical farming is that it produces far more food per square foot than traditional methods. Instead of spreading one layer of crops over acres, a hydroponic vertical farm stacks multiple layers in the same footprint. This 3D use of space leads to remarkable yield density. Studies show that vertical farming facilities can yield up to 11.7 kg of crops per square meter each year, an impressive boost in productivity compared to conventional farming.
This land efficiency is especially valuable as arable land becomes scarce. Vertical farms can be built in warehouses, rooftops, or even marginal land where field farming isn’t possible. By growing upward, they can save 70-95% more land space than traditional farming while still producing the same volume of crops. High-density planting ensures every cubic meter is optimized for photosynthesis, with trays stacked several stories high.
2. Year‑Round Production & Continuous Harvests
One of the greatest vertical farming pros is its ability to deliver year-round food production regardless of season or weather. Traditional farms depend on natural cycles, often producing only one or two harvests annually, with downtime in winter or dry seasons. In a vertical farm, crops thrive in controlled conditions 24/7, so there’s no off-season.
Controlled environments also shorten growth cycles. As per reports, lettuce that takes 60+ days outdoors can be harvested 4–5 times per year indoors, thanks to optimized light and climate. Many vertical farms stagger plantings, ensuring weekly harvests that keep shelves stocked without seasonal gaps.
This reliability extends to external shocks. Frosts, droughts, or storms won’t disrupt production; your crops keep growing under LEDs, whether it’s January or July. Even repurposed warehouses or shipping containers can become hydroponic vertical farms, bringing fresh, local produce directly into urban communities year-round.
3. Dramatically Reduces Water Use
How Does Vertical Farming Save Water? One of the most significant environmental benefits of vertical farming is its incredible water efficiency. Indoor hydroponic and aeroponic systems recirculate water in a closed loop, using 70–95% less water than traditional farming. Since water is delivered directly to the roots and recaptured, almost nothing is wasted.
This efficiency is critical because agriculture consumes about 70% of the world’s freshwater. By cutting water use so dramatically, vertical farming eases pressure on rivers and aquifers and makes farming viable even in drought-prone regions. To illustrate: growing a head of lettuce in a vertical hydroponic system may require less than 1 liter, compared to 15–20 liters in soil-based farming.
4. Pesticide‑Free & Safer Food
One of the key vertical farming pros is the ability to grow crops without pesticides or herbicides. In open fields, crops face insects, weeds, and diseases, leading to heavy chemical use. In a sealed vertical farm, pests rarely enter; no soil to harbor them, filtered air systems, and biological controls (like ladybugs) when needed. The result is food that’s clean and often marketed as grown without pesticides, a strong appeal for health-conscious consumers.
Moreover, the benefits of indoor vertical farming also extend to the environment and worker safety. With no chemical sprays, there’s no runoff polluting soil and water, no harm to beneficial insects, and no toxic exposure for farm staff. Beyond that, indoor farms significantly reduce contamination risks from E. coli or Salmonella, which often affect field-grown greens.
5. Optimizes Energy & Resource Efficiency
One of the most significant vertical farming benefits and challenges lies in energy and resource efficiency. Vertical farms use automation, sensors, and AI to fine-tune growing conditions. Lighting, water, and nutrients are delivered exactly when needed, minimizing waste. Modern LED grow lights emit only the red and blue wavelengths plants use, cutting energy use by around 15% while boosting growth. Water and nutrients are recycled, while climate systems manage heat efficiently, sometimes even shifting high-energy tasks to off-peak hours.
However, the challenge is energy consumption. Producing 1 kg of lettuce indoors can require ~38 kWh compared to ~5.4 kWh in a greenhouse. This higher footprint is a common criticism. Yet, technology is closing the gap: advanced LEDs, AI-driven climate control, renewable energy integration (solar, wind), and waste heat capture systems are making vertical farms greener. Many facilities now recapture heat from LED lights and equipment to warm growing areas, while solar panels and wind power reduce reliance on grid electricity. The result is consistent yields, precise resource use, and an increasingly sustainable agriculture model.
6. Shortens Supply Chains & Reduces Food Miles
One of the most substantial vertical agriculture farming advantages is localizing food production. By building farms close to cities, crops travel fewer miles from harvest to plate. This dramatically reduces transport emissions and logistics costs while delivering fresher produce to consumers. Instead of lettuce taking a week to cross the country, vertical farms can harvest and deliver within 24–48 hours, keeping both freshness and nutrition intact.
Leading companies strategically place facilities within a 200-mile radius of their markets, cutting 5–7 days of transit common in traditional farming. Shorter agriculture supply chains also reduce food waste, since spoilage and damage during long-haul shipping are minimized. With food grown close to cities, retailers get longer shelf life and consumers enjoy tastier, more nutritious greens.
7. Lower Labor Costs & Automation
One of the major advantages of vertical farming is reduced reliance on manual labor. Traditional farming requires large crews for planting, weeding, and harvesting, but a hydroponic vertical farm leverages robotics and automation to handle much of this work. Robots used in farms help to sow seeds, conveyor systems move crops, and AI-powered machines identify and harvest ripe produce. This shift means a small team of technicians can manage output comparable to a large field crew, resulting in significantly lower labor costs.
Automation also improves consistency and crop quality; robots don’t fatigue, reducing errors while ensuring higher yields. Work conditions are safer too, as employees operate in climate-controlled, pesticide-free facilities instead of enduring extreme heat or heavy machinery. Roles shift toward supervision, engineering, and technical operation, making agriculture more attractive to tech-savvy workers.
8. Resilience to Weather & Climate Shocks
Unlike traditional farming, indoor vertical farms remain unaffected by adverse weather conditions. Climate change brings droughts, floods, storms, and heatwaves that can devastate outdoor crops, but a hydroponic vertical farm continues producing food in its sealed, climate-controlled environment. Whether it’s a drought drying up fields or a hurricane destroying harvests, vertical farms maintain steady output.
This reliability is why vertical farming is essential for future food security. Countries with harsh climates like the UAE, Singapore, and northern Canada already use vertical farms to reduce imports and secure local supply. By creating ideal microclimates, they can grow greens in deserts or Arctic regions, ensuring fresh produce year-round.
Beyond weather, vertical farms also shield crops from wildfire smoke, pests, and dirty irrigation water, reducing contamination risks. In a world facing climate uncertainty, vertical farming acts as a food insurance policy, guaranteeing communities fresh, safe produce even when traditional agriculture fails.
9. Sustainable & Environmentally Friendly Growth
Why is vertical farming good for the environment? By stacking production indoors, farms produce acres of crops in a single building, easing pressure on forests, wetlands, and grasslands. This preservation of natural ecosystems delivers crucial environmental benefits of vertical farming, protecting biodiversity and reducing soil degradation. With nearly one-third of arable land lost in the past 40 years, shifting some production indoors helps safeguard soil for future generations.
Vertical farms also cut pollution. Unlike traditional farms that create fertilizer runoff and erosion, indoor systems recirculate water with zero waste. There’s no nitrogen leaching or algal blooms, and no heavy machinery burning diesel in the fields. By being local, they also slash food miles, lowering emissions from long-haul trucking.
10. Economic & Community Opportunities
The economic benefits of vertical farming go well beyond efficiency. This industry is fueling a fast-growing Agtech sector that attracts investment, creates skilled jobs, and opens new business models. Globally, the vertical farming market is projected to reach $12–13 billion by 2026, with the U.S. alone expected to hit nearly $19 billion by 2028. Major investors and entrepreneurs are backing startups that sell premium produce, license farming technology, and build software for farm management.
Vertical farms also revitalize urban areas by converting abandoned warehouses and factories into productive hubs. They create jobs like hydroponic technicians, engineers, and logistics coordinators, roles that blend agriculture with technology. Community engagement is another win, while high capital and energy costs remain hurdles, creative financing models, modular designs, and government grants are helping overcome barriers.
How AI is Shaping Vertical Farming to Enhance Efficiency and Yield?
How Does AI Help in Vertical Farming? AI is transforming vertical farming from a novel growing method into a highly efficient food system. Modern farms now collect thousands of data points daily from climate sensors to plant imagery, and AI turns this raw information into actionable insights. By bridging technology with cultivation, AI enables farmers to not just grow plants but to manage entire ecosystems with precision.
Intelligent crop monitoring: AI-powered cameras and sensors track each plant, detecting nutrient deficiencies, pests, or diseases by analyzing leaf color and texture. Early crop disease detection enables quick corrective action, preventing problems from spreading and protecting yields.
Automated climate control: Machine learning algorithms adjust lighting, humidity, and temperature in real time, ensuring crops grow under ideal conditions. These systems even optimize energy use by running tasks when electricity is cheapest, lowering costs while improving sustainability.
Yield prediction and resource optimization: By forecasting harvest times and quantities, AI streamlines staffing, logistics, and sales. It can also simulate “what-if” scenarios to fine-tune nutrients, lighting, or planting schedules.
In short, AI acts as a 24/7 farm manager, delivering consistent results and maximizing the benefits of vertical farming for efficiency, sustainability, and profitability.
Wrapping it Up
So, why is vertical farming good for the future? It tackles today’s toughest agricultural challenges: limited land, soil degradation, and climate change, while delivering fresh, local food. Vertical farming pros include year-round harvests, efficient water use, reduced pesticide reliance, and crops grown close to cities for peak freshness. Where high energy costs and limited crop variety remain hurdles, this model complements traditional farming rather than replacing it.
For farm owners, greenhouse managers, or ag-tech entrepreneurs, the takeaway is clear: vertical farming can diversify your strategy and strengthen local food systems. As technology improves, the benefits of vertical farming will only expand, making it a key driver of sustainable food production in the years ahead.
FAQs
What Are the Main Benefits of Vertical Farming?
The key benefits of vertical farming include maximizing space to achieve higher yields, conserving water through closed-loop systems, and enabling consistent, year-round production. Since crops grow indoors under controlled conditions, the need for pesticides is reduced, leading to healthier and more sustainable produce.
Can Vertical Farms Be Set Up in Urban Areas?
Yes. Vertical farming in urban areas is already proving successful, with farms built inside warehouses, high-rises, and even repurposed city buildings. These systems bring fresh produce directly to local communities using fresh produce ERP, reduce food miles, and make better use of limited city space.
How Does Vertical Farming Contribute to Reducing Food Waste?
Vertical farming reduces food waste by producing crops closer to consumers, cutting down on transportation and spoilage. Controlled environments also enable precise harvest planning, ensuring supply matches demand and minimizing both overproduction and waste.
Is Vertical Farming Suitable for Growing All Types of Crops?
While not ideal for every crop, vertical farming crops like leafy greens, herbs, strawberries, and tomatoes thrive in hydroponic and aeroponic systems. These high-value, fast-growing plants adapt well to controlled conditions and deliver strong returns for growers.
What Are the Common Challenges of Vertical Farming?
Some of the main vertical farming challenges include high setup and energy costs, limited crop variety, and the need for skilled labor and advanced technology. Since farms rely heavily on systems like climate control and lighting, regular monitoring and maintenance are critical.
How Much Does It Cost to Set Up a Vertical Farm?
The vertical farming cost depends on scale, technology, and location, but it typically ranges from $1,000 to $35,000 per square meter of growing area. Expenses include lighting, automation, climate systems, and labor. Larger facilities with advanced technology can run into millions of dollars.