Feeding the world in the face of climate change, resource scarcity, and an expanding population is one of agriculture’s defining challenges. The United Nations projects that the global population will swell to 9.7 billion by 2050, nearly two billion more humans to feed than today. Conventional farming methods alone cannot deliver the productivity gains and sustainability improvements required to meet this demand. At the same time, agriculture is under pressure to reduce its water and energy footprints; irrigation alone uses 70 % of the world’s fresh water.
In this context, smart farming technology has emerged as the backbone of the digital agriculture revolution. By combining sensors, connectivity, data analytics, and automation, smart farms can monitor crops and livestock in real time and use data‑driven insights to optimize every operation. This guide explains what smart farming technology is, how it differs from precision agriculture, the technologies and use cases shaping modern agriculture, and practical steps to adopt these innovations.
What Is Smart Farming Technology?
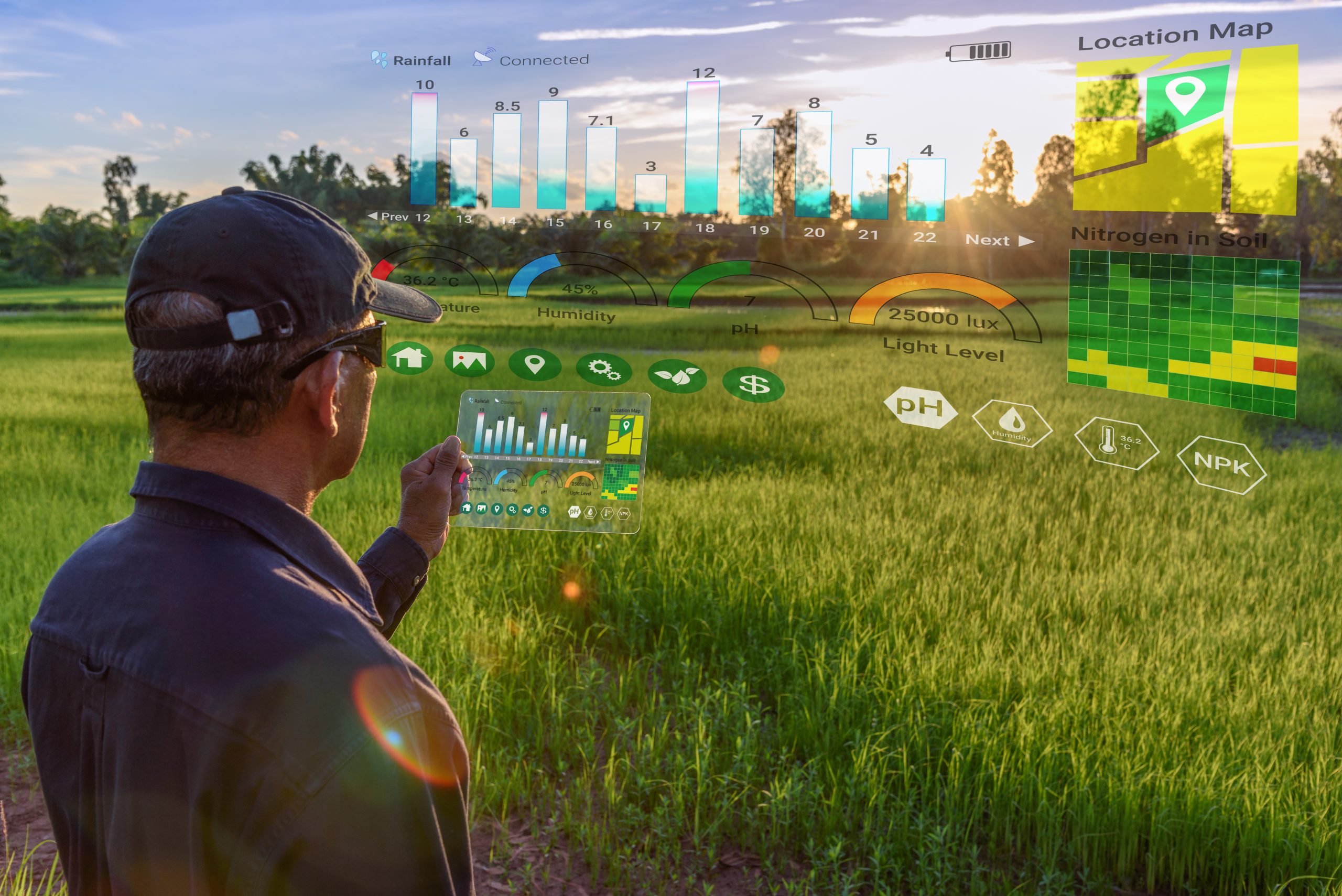
Smart farming technology refers to the integration of Internet‑of‑Things (IoT) sensors, drones, artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and data analytics to monitor and manage farming operations more precisely than ever before. It goes beyond installing a few sensors; it connects all equipment, fields, and animals into an intelligent network. Smart devices continuously observe soil moisture, weather, plant health, and livestock behaviour. Cloud‑hosted platforms then diagnose conditions by applying agronomic models and machine‑learning algorithms. Based on these diagnostics, the system decides which actions are needed, such as adjusting irrigation schedules, applying fertilizer only where required, or scheduling preventive livestock health treatments.
Finally, automated systems act, whether by opening and closing irrigation valves, instructing autonomous tractors, or sending alerts to farm managers. This complete observation–diagnostics–decision–action cycle underpins the “smart farm” concept and distinguishes it from single‑use technologies. Smart farming aims to optimize resource use, increase yields, and reduce environmental impacts, making it a key pillar of climate‑smart agriculture.
Precision Agriculture vs Smart Farming
Precision agriculture technology is a subset of smart farming. It focuses on applying inputs, such as seed, fertilizer, water, and crop protection products, at the right time, rate, and place to minimize waste and maximize yield. Technologies include guidance autosteering, variable‑rate equipment, and yield monitors. These tools are now mainstream, as over half of major crops, and today, 52% of midsize and 70% of large farms use auto-steer systems.
Meanwhile, smart farming encompasses precision agriculture and extends to continuous sensing, connectivity, AI‑driven analytics, and automation across crops, livestock, and supply chains. It connects data from multiple sources, including soil sensors, drones, satellites, and wearables, into integrated decision‑support systems.
While precision agriculture concentrates on variable‑rate application, smart farming aims to create a self‑optimizing agricultural ecosystem. Both approaches improve efficiency, but smart farming leverages the full power of digital technologies to transform how farms are managed.
How Smart Farming Works: The IoT-Driven Cycle
Smart farming operates as a continuous data-driven loop. First, sensors and IoT devices collect information: soil moisture probes, weather stations, cameras, drones, and satellites gather data on field conditions and crops. This raw data is transmitted via networks (cellular, Wi-Fi, LPWAN) to cloud servers.
Observation: Sensors, drones, and cameras gather continuous data on soil moisture, nutrient levels, temperature, humidity, plant growth, weed pressure, and animal health. Livestock wearables monitor body temperature, rumination, and mobility, while environmental sensors track microclimate conditions.
Diagnostics: Cloud‑based platforms and farm‑management software aggregate sensor data and apply AI models. Machine‑learning algorithms detect anomalies, such as stress signals in plants or irregular feeding patterns in animals.
Decision: The system recommends optimal actions based on diagnostics. For example, if soil moisture drops below a threshold, it can suggest targeted irrigation; if a temperature sensor indicates a heat event, it can alert farmers to adjust greenhouse shading.
Action: Automation executes the decisions. Drip irrigation controllers open valves; drones spray fertilizer or pesticides only where needed; autonomous tractors perform cultivation; and farmers receive alerts via mobile apps.
Key Smart Farming Technologies with Examples
Modern smart farms employ a suite of technologies facilitating various aspects of agriculture. Below are core examples that you may deploy at your farm:
Soil and Microclimate Sensors
Soil moisture and nutrient sensors provide real‑time data on water availability, salinity, and nutrient levels in the root zone. Weather stations measure temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, and solar radiation. By combining these data, farmers can schedule irrigation more precisely and apply fertilizer only where needed. Accurate sensing reduces over‑watering, which is critical in arid regions, and helps prevent nutrient runoff into waterways.
Smart Irrigation Systems
Conventional flood irrigation is wasteful; water flows through fields regardless of plant needs. Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the root zone and can reduce water consumption by 20–60 %. When connected to smart valves and IoT controllers, irrigation is adjusted based on soil moisture and weather forecasts. Moreover, the precision irrigation controller achieved 44% water savings and 38% energy savings compared with traditional drip irrigation. For desert farming or drought‑prone areas, such technology helps farmers produce more “crop per drop”.
Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
As a part of smart farming technology, drones in agriculture equipped with multispectral cameras capture high‑resolution images for crop health monitoring, yield prediction, and mapping. They can detect stress, nutrient deficiencies, or pest infestations before symptoms are visible to the naked eye. UAVs also enable targeted spraying and seeding, reducing labour and chemical use. Autonomous drones can cover large areas quickly, providing timely data for decision-making.
Precision Pest and Weed Control
Uncontrolled weeds and pests can significantly reduce yields. Smart farms use computer‑vision systems and AI models to identify weeds and crop diseases early. For example, deep learning disease detection frameworks can diagnose leaf diseases with accuracy, allowing timely interventions. Spot‑spraying robots or drones apply herbicides only where weeds are present, reducing chemical usage and environmental impact.
Livestock Monitoring & Wearables
Precision livestock farming technologies, such as wearable devices that monitor cattle, sheep, and poultry for temperature, heart rate, rumination, and location. By analyzing these data streams, farmers can detect health issues, estrus, or calving events earlier, reducing mortality and improving productivity. Automated feeding systems deliver the right ration for each animal based on weight and growth targets.
Smart Greenhouses & Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Greenhouse management systems employ sensors and actuators to control temperature, humidity, lighting, and nutrient delivery. AI algorithms adjust these parameters automatically to create optimal growing conditions, resulting in faster growth cycles and higher yields. In vertical farms, sensors monitor nutrient film solutions and LED lighting, enabling year‑round production close to urban markets with minimal land usage.
Farm Management Software & Data Platforms
Farm management software platforms integrate data from sensors, drones, weather feeds, and machinery. They provide dashboards, alerts, and analytics that help farmers track crop development, manage inputs, forecast yield, and implement harvest planning for better yields. Many systems integrate with financial tools, enabling better budgeting and reporting. They also support compliance reporting for sustainability standards.
Robotics & Automation
Autonomous tractors, harvesters, and robots reduce labour needs and perform tasks with high precision. Self‑driving tractors guided by GPS and machine vision can plant and cultivate with centimetre‑level accuracy. Robotic milking systems automate labour‑intensive steps, and the labour‑saving potential is a critical reason farmers adopt such technologies. Smaller field robots weed or harvest specialty crops gently, addressing labour shortages and safety concerns.
Supply‑Chain and Traceability Solutions
Smart farming extends beyond the farm gate. Blockchain and RFID systems, supply chain systems track produce from the field to the consumer, improving food safety and provenance. Sensors in transport vehicles monitor temperature and humidity to ensure fresh produce quality. Consumers increasingly demand transparency about how food is grown; smart traceability tools provide the necessary data.
Latest Smart Farming Technology Trends
Modern agriculture is rapidly becoming a data-driven ecosystem where every seed, sensor, and satellite works in sync to optimize yield and sustainability. Let’s explore the emerging technologies reshaping the field and what they mean for you as a grower or agribusiness leader.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI in agriculture is the brain behind today’s smart farms. ML algorithms process millions of data points from soil sensors, drones, and cameras to predict crop health, pest outbreaks, and irrigation needs. Predictive analytics also forecasts yield and market demand, allowing smarter planting and pricing decisions.
Big Data Analytics
Each connected farm can generate over 500,000 data points per day, from soil moisture to machinery telemetry. Through effective farm data management, big data platforms consolidate these readings to create a 360-degree view of field performance. You can identify under-performing plots, calculate ROI per acre, and benchmark productivity across seasons, all in real time.
Satellites & Remote Sensing
High-resolution satellite imagery and UAV mapping in farm management reveal nutrient deficiencies, crop stress, and even early disease signs invisible to the naked eye. When combined with weather models, they enable precision spraying and fertilizer planning that saves resources and improves soil health.
Robotics & Autonomous Machinery
Driverless tractors, drone sprayers, and robotic harvesters reduce labor dependency and increase operational safety. Moreover, drones can spray fertilizers 40–60 times faster than manual methods, drastically cutting time and fuel costs.
5G and Edge Computing
With 5G connectivity and on-device data processing, latency drops to near zero. Machines communicate instantly, supporting real-time decisions for irrigation, logistics, and crop monitoring even in remote fields.
Blockchain & Digital Twins
Blockchain ensures every input from seed to shipment is traceable and tamper-proof, giving consumers confidence in food origin. Digital twin simulations mirror entire farms virtually, letting managers test scenarios before applying them in the field.
Benefits of Smart Farming Technology as per ROI
Smart farming is not just about technology for technology’s sake; it delivers tangible benefits. Although the initial investment can be significant, the combination of higher yields, lower input costs, and reduced environmental footprint often leads to a compelling return on investment over the long term.
Yield increases and profitability: Farmers using precision agriculture technologies have seen around a 4% increase in crop production. When combined with smart‑farm data analytics, these yield gains translate into higher profitability without expanding farmland.
Input efficiency: Precision application improves fertilizer placement efficiency by 7% and reduces herbicide use by 9%. Labour‑saving technologies such as robotic milking lower operating costs and reduce operator fatigue.
Environmental sustainability: Precision practices reduce fossil fuel use by about 6% and water use by 4%. By avoiding the over‑application of chemicals, smart farming helps prevent nutrient runoff and conserves water resources. As per the estimate, current adoption could avoid 2 million acres of cropland expansion, 30 million pounds of herbicide, and 100 million gallons of fossil fuel.
Better decision‑making: Real‑time data and predictive models enable farmers to make informed decisions rather than relying on intuition or historical averages. Timely disease detection allows interventions before yields are lost.
Resilience: Smart farms are better equipped to handle climate variability and labour shortages. Automated systems continue operations when human labour is scarce, and data‑driven adjustments help farms adapt to extreme weather events.
In this Third Green Revolution, farms will be predictive, adaptive, and regenerative, leveraging data not only to optimize yields but also to enhance soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. For farmers and agribusinesses, the future lies in embracing digital tools and building resilient, data‑driven operations.
Challenges & Solutions to Deploy Smart Farming Agriculture Technology
Despite its promise, smart farming faces barriers. By addressing these barriers, policymakers, researchers, and industry can accelerate adoption and ensure that smart farming benefits farms of all sizes.
High up‑front costs: Advanced sensors, drones, and automation can be expensive. Smaller farmers may lack access to capital or financing. Only 27% of U.S. farms used precision agriculture practices in 2023, in part because of cost barriers.
Solution: Governments can provide grants, loans, or tax credits to lower acquisition costs. The GAO suggests expanding eligibility for existing programs and creating new incentives to encourage adoption.
Connectivity and infrastructure: Rural broadband gaps limit data transmission. Real‑time analytics require reliable internet and power.
Solution: Public–private partnerships can expand rural broadband and 5G coverage. Low‑power wide‑area networks (LPWANs) like LoRaWAN offer cost‑effective connectivity for sensors.
Data privacy and ownership: Farmers may be hesitant to share data with technology providers. There are concerns to some extent that data sharing and ownership can hinder adoption.
Solution: Clear agreements specifying data ownership, usage rights, and privacy protections build trust. Industry consortia can develop open standards.
Lack of standards and interoperability: Proprietary systems may not integrate, increasing complexity and locking farmers into specific vendors.
Solution: Standards bodies can promote equipment compatibility, enabling farmers to mix and match devices.
Skills and training: Adopting digital tools requires new skills. Farmers need support to interpret data and maintain equipment.
Solution: Agricultural extension agencies, universities, and technology vendors are offering on‑farm demonstrations, online courses, and technical support.
How Folio3 Can Help You Implement Smart Farming Technology
As a trusted partner to agribusinesses worldwide, Folio3 AgTech helps turn smart‑farming aspirations into reality. We integrate sensor data, drone imagery, weather feeds, and ERP systems into a single dashboard, providing real‑time insights and predictive analytics. Also, we specialize in designing custom IoT solutions from soil moisture networks to livestock wearables and integrating them with existing infrastructure.
Our expertise in machine learning and artificial intelligence enables automated disease detection, yield forecasting, and resource optimization tailored to specific crops and geographies. Whether you are exploring precision agriculture, building a smart greenhouse, or deploying robotic systems, our team collaborates with you to define goals, prototype solutions, and scale them across your operations.
By partnering with Folio3, you gain access to technical know-how, implementation support, and ongoing training, empowering your farm to thrive in the digital age.
Conclusion
Smart farming technology marks a transformative shift in agriculture. By connecting sensors, machines, and analytics into a responsive feedback loop, farms can increase yields, conserve resources, and enhance sustainability. Precision practices already deliver measurable benefits and significant reductions in water, fuel, and pesticide use. Yet adoption remains uneven due to cost and infrastructure challenges. Overcoming these barriers requires coordinated efforts: financial incentives, rural broadband expansion, data governance, and training. With the right support, smart farming can form the foundation of the Fourth Agricultural Revolution, enabling agriculture to feed a growing population while restoring ecosystems. Farmers who embrace data‑driven tools today will lead the way toward a resilient and regenerative food system.
FAQs
How Is AI Used In Smart Farming?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) powers smart farming by helping farmers make faster, data-backed decisions. From predicting weather patterns and detecting crop diseases to automating irrigation and resource use, AI ensures higher yields with less waste. It turns complex data into practical actions that improve farm efficiency and sustainability.
Is Smart Farming The Future?
Absolutely. Smart farming represents the next era of agriculture, where technologies like AI, IoT sensors, robotics, and big data work together to make farming more productive, sustainable, and resilient. It empowers farmers to grow more with fewer inputs while reducing environmental impact, making it a key driver of agriculture’s digital transformation.
How Does Smart Irrigation Technology Help In Desert Farming?
Smart irrigation systems are a game-changer for desert and arid regions. They use real-time soil moisture and weather data to deliver precise amounts of water directly to plant roots only when needed. This approach cuts water use by up to 50%, saves energy, reduces soil salinity, and boosts crop yield, all while lowering manual labor and maintenance costs.
How Can Small And Medium Farms Adopt Smart Farming Technologies?
Smaller farms can begin their smart farming journey without heavy investments. Start with low-cost tools like soil sensors, weather-tracking apps, or automated irrigation systems. Many governments and Agtech programs offer subsidies or community-based solutions to support adoption. Cloud-based farm management platforms also provide affordable ways to digitize operations and improve productivity step-by-step.