The world’s farms stand at a pivotal moment. A perfect storm of challenges—climate change, burgeoning populations, and the imperative of food security—demands a radical overhaul of how we cultivate and nourish our planet.
The traditional plow and seed are being complemented, if not replaced, by a technological revolution that is redefining agriculture. This transformation is no longer a distant horizon; it’s the present landscape.
To thrive in this new era, farmers and agribusinesses must navigate a complex web of emerging future trends in agriculture. In this blog, we delve into the top 10 current trends in agriculture of 2026, offering insights to help you stay ahead of the curve and contribute to a sustainable, productive, and resilient food system.
1. Digital Agriculture
The era of guesswork in agriculture is yielding to the precision of data. Digital agriculture is the usage of technology to manage and optimize every facet of farming. It’s about transforming the fields into data-rich environments where decisions are steered by insights rather than intuition.
Technologies
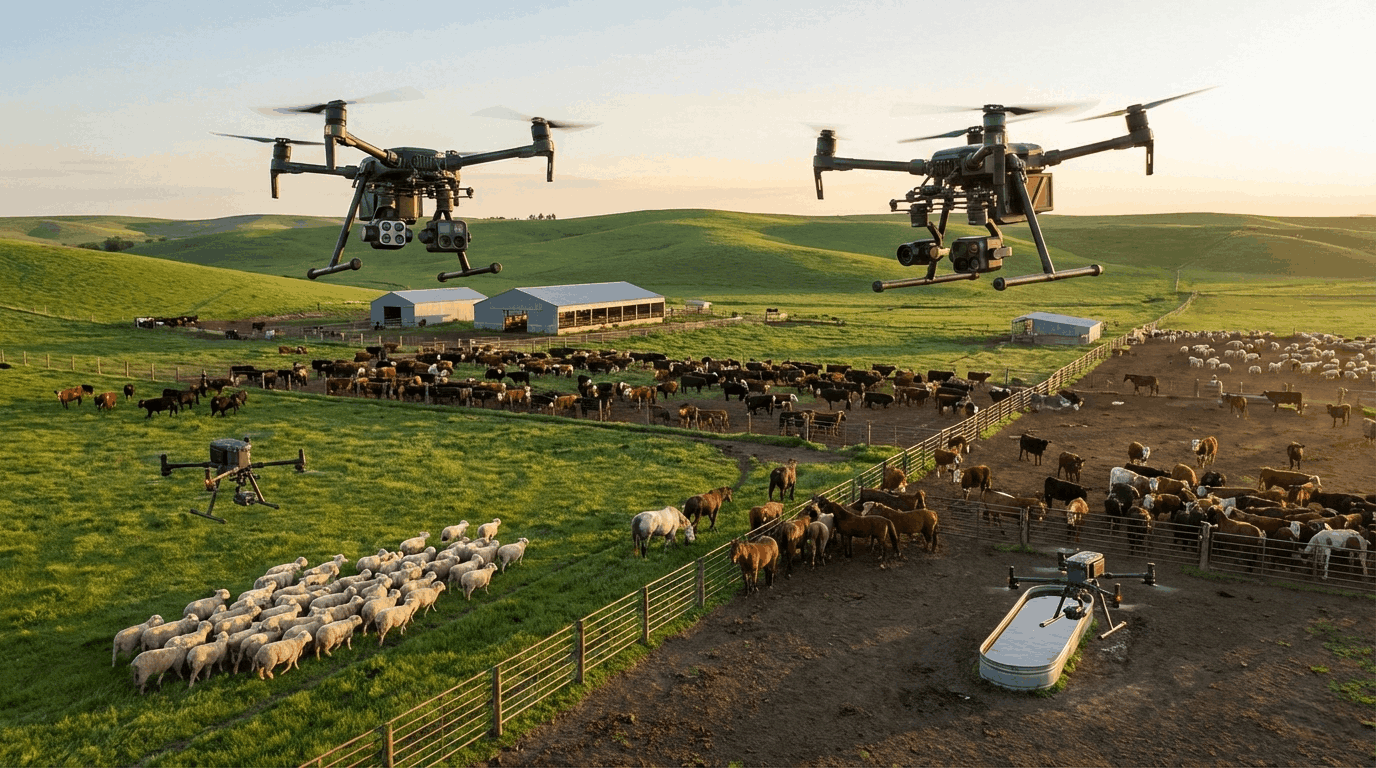
At the forefront of this revolution are Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which are like the farm’s nervous system. These sensors, scattered across fields, collect real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels.
Drones, with their bird’s-eye view, provide high-resolution imagery to monitor crop health, detect pests and diseases, and optimize planting patterns. And then there are robotic harvesters, machines of incredible precision that can work tirelessly, reducing labor costs and minimizing crop damage.
Benefits
The payoff is immense. Farmers can pinpoint exactly when and where to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
Predictive analytics, powered by this data, can forecast yields, optimize harvesting schedules, and even predict disease outbreaks. The net result is a boost in productivity, reduced environmental impact, and greater profitability.
Example
A prime example is the deployment of IoT-based sensor stations by companies like ICL. These devices provide granular insights into soil and crop conditions, enabling farmers to tailor their management practices with unprecedented accuracy. It’s a testament to how digital agriculture is empowering farmers to cultivate more with less, ensuring a sustainable future for our food supply.
2. Use of Digital Twins & Generative AI
The agricultural landscape is increasingly reliant on digital tools that offer a glimpse into the future. Enter digital twins and generative AI, a powerful combination that is revolutionizing farming practices.
Applications
A digital twin is essentially a virtual replica of a physical system. In agriculture, this could be a field, a crop, or even an entire farm. By feeding real-time data into these digital models, farmers can create highly accurate simulations of how their operations will respond to various conditions.
This is where generative AI in agriculture comes into play. When you start analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, AI algorithms can predict crop yields, optimize resource allocation, and even forecast the impact of climate change.
Benefits
The applications of this technology are far-reaching. Farmers can simulate different planting scenarios, experiment with various crop rotations, and assess the potential impact of weather events, all without risking real-world losses.
This enables more informed decision-making, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs. Moreover, by anticipating challenges like pests, diseases, or droughts, farmers can proactively implement mitigation strategies, safeguarding their crops and livelihoods.
Example
Companies like ICL are at the forefront of this technological advancement. Their AI models, in collaboration with Sentera, are capable of predicting crop needs based on real-time data and environmental factors.
This level of precision farming not only boosts yields but also minimizes environmental impact. As digital twins and generative AI mature, we can expect to see even more sophisticated applications that will transform agriculture into a highly predictive and sustainable industry.
3. Regenerative Agriculture
A growing awareness of the environmental impact of conventional agriculture is driving a shift towards more sustainable practices. Regenerative agriculture is a holistic approach that focuses on restoring and enhancing soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience.
Practices
Key practices in regenerative agriculture include adaptive grazing, where livestock are managed to mimic natural grazing patterns, and no-till farming, which preserves soil structure and organic matter.
Additionally, reducing reliance on synthetic chemicals is a core principle, as it promotes soil health and reduces pollution.
Benefits
The benefits of regenerative agriculture are manifold. By improving soil fertility, farmers can enhance crop yields and reduce the need for chemical inputs. Moreover, healthy soils act as carbon sinks, helping to mitigate climate change.
Furthermore, by fostering biodiversity, regenerative agriculture supports ecosystem services such as pollination and pest control.
Example
Many farmers are already embracing these principles. For instance, ICL has been working with farmers to adopt no-till practices, which have shown promising results in terms of reduced erosion, improved water retention, and increased soil organic matter.
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and food security, regenerative agriculture offers a path toward a more sustainable and resilient food system.
4. Precision Agriculture
Every corner of a field tells a unique story. Soil composition, topography, and crop health can vary significantly, even within short distances. Precision agriculture is the art and science of recognizing and responding to these variations.
Technologies
Using technologies like drones, satellite imagery, and advanced sensors, farmers can create detailed maps of their fields, identifying areas with specific needs.
This information is then used to apply inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides with pinpoint accuracy. Precision weed management systems, for example, can target specific weeds without harming the desired crop, minimizing chemical use.
Benefits
The rewards of precision agriculture are substantial. By optimizing resource allocation, farmers can maximize yields while reducing costs. Targeted interventions also minimize environmental impact by preventing the overuse of chemicals.
Moreover, the data collected through precision agriculture provides invaluable insights into crop performance and field conditions, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions for future seasons.
Example
Companies like Sentera are at the forefront of precision agriculture, offering drone-based systems for precise herbicide application.
These technologies are transforming the way farmers manage their fields, moving from a one-size-fits-all approach to a tailored care model that maximizes efficiency and sustainability.
5. Agricultural Robotics
The backbreaking work of farming is undergoing a technological transformation. Agricultural robotics is the deployment of autonomous machines to handle the repetitive tasks that have traditionally relied on human labor.
Applications
From planting seeds to harvesting crops, weeding to livestock management, robots are taking on an increasingly important role. Autonomous tractors can navigate fields with precision, while robotic harvesters can work tirelessly without breaks.
These machines are equipped with sensors and artificial intelligence, allowing them to adapt to varying field conditions and optimize their performance.
Benefits
The benefits of agricultural robotics are clear. By reducing reliance on human labor, farmers can lower costs and ensure consistent operations. Moreover, robots can work in challenging conditions, such as extreme heat or cold, without compromising safety.
Additionally, the use of robotics can free up human workers to focus on higher-value tasks, such as crop monitoring and quality control.
Example
StartUs Insights highlights the growing trend of autonomous tractors and robotic harvesters on large-scale farms. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated agricultural robots that will reshape the farming landscape.
6. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is weaving a digital tapestry across the agricultural landscape. This network of interconnected devices collects and shares real-time data, transforming the way farms are managed.
Applications
From tracking soil moisture levels to monitoring weather patterns, IoT sensors in agriculture offer unparalleled visibility into field conditions. This data can be used to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, leading to significant resource savings.
Additionally, IoT-enabled devices can automate tasks such as opening and closing greenhouse vents, reducing manual labor and ensuring optimal growing conditions.
Benefits
The benefits of IoT in agriculture extend beyond efficiency. By providing real-time insights, farmers can make timely interventions, preventing problems before they escalate. For example, early detection of disease or pest outbreaks can save crops and minimize losses.
Example
StartUs Insights highlights the increasing adoption of IoT sensors for remote monitoring of greenhouses and farms. As connectivity improves and sensor technology becomes more affordable, the potential applications of IoT in agriculture are vast and exciting.
7. Vertical Farming
As land becomes increasingly scarce and urbanization expands, vertical farming is emerging as a promising solution. This innovative approach involves cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers, often within controlled environments like warehouses or skyscrapers.
Advantages
By ignoring the traditional horizontal layout, vertical farming maximizes space efficiency. This is particularly advantageous in urban areas where land is at a premium.
Additionally, by controlling factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, vertical farms can reduce water usage and produce crops year-round, regardless of external weather conditions.
Technologies
Technologies like LED lighting, hydroponics, and aeroponics are essential to the success of vertical farming. LED lights provide the necessary spectrum of light for plant growth, while hydroponics and aeroponics cultivate plants without soil, optimizing water and nutrient use.
Example
The impact of vertical farming is already being felt. Urban centers are witnessing the rise of vertical farms that produce fresh produce close to consumers, reducing transportation emissions and ensuring product freshness.
As technology advances and consumer demand for locally grown food increases, vertical farming is poised to become a significant component of the global food system.
8. Sustainable Food Production
The future of food production hinges on sustainability. This means producing food in a way that ensures long-term food security while minimizing environmental impact. It’s about striking a balance between feeding a growing population and preserving our planet for future generations.
Technologies
To achieve this, a multifaceted approach is required. Incorporating biodegradable packaging into the supply chain is a crucial step. By reducing plastic waste, we can mitigate pollution and protect ecosystems.
Sustainable pest control methods, such as biological control agents and crop rotation, can minimize the use of harmful chemicals and preserve beneficial insects. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources into farm operations can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and lower energy costs.
Benefits
The benefits of sustainable food production are far-reaching. By reducing our carbon footprint and conserving resources like water and soil, we create a healthier planet.
Furthermore, sustainable practices contribute to biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. As consumers become increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their food choices, there is a growing demand for products produced in a sustainable manner.
Example
While the transition to sustainable food production presents challenges, it also offers significant opportunities for innovation and growth.
By adopting these practices, the agriculture industry can not only ensure food security but also play a vital role in addressing climate change and protecting our natural resources.
9. Advanced Crop Genetics
The genetic makeup of our crops is undergoing a revolution. Advanced crop genetics, powered by technologies like genetic engineering and CRISPR, is unlocking the potential to create plants with enhanced traits.
Focus Areas
By manipulating the DNA of crops, scientists can develop varieties that are better equipped to withstand the challenges of a changing climate. Drought resistance, for example, is a critical trait as water scarcity becomes more prevalent.
Similarly, crops with built-in pest resistance can reduce the need for chemical pesticides, benefiting both farmers and consumers. Beyond resilience, genetic engineering can also improve crop yield, nutritional value, and taste.
Benefits
The implications of advanced crop genetics are far-reaching. Higher productivity can help feed a growing population, while climate-resilient crops can safeguard food security.
Improved food quality can enhance human health and nutrition. However, it is essential to approach this technology with caution, considering ethical and environmental implications.
Example
Companies like ICL are at the forefront of developing crops that can withstand extreme weather conditions. These advancements are crucial for ensuring a stable and sustainable food supply in the face of climate change. As our understanding of genetics continues to expand, the possibilities for improving crops are virtually limitless.
10. Big Data and Analytics
The agricultural industry is generating vast amounts of data, from satellite imagery to sensor readings and yield records. Big data and analytics provide the tools to harness this information and transform it into actionable insights and keep up with the latest sustainable agriculture trends.
Applications
By analyzing historical data and real-time information, farmers can predict yields, optimize planting and harvesting schedules, and identify areas for improvement.
Soil health analysis can help determine nutrient deficiencies and inform fertilization practices. Moreover, understanding farming trends can assist in making informed decisions about crop selection and pricing.
Benefits
The benefits of big data and analytics extend beyond the farm. By optimizing operations and reducing waste, farmers can improve profitability and sustainability. Additionally, data-driven insights can support the development of new agricultural technologies and practices.
Example
Platforms that provide comprehensive analytics for farm management are becoming increasingly common. These tools empower farmers to make data-driven decisions and unlock the full potential of their operations.
As data collection and analysis capabilities continue to advance, the role of big data in agriculture will only grow in importance.
Conclusion
The agricultural industry is on the cusp of a transformative era. The 10 trends in agriculture outlined above are not mere possibilities but the building blocks of a sustainable, productive, and resilient food system.
By embracing digital technologies, sustainable practices, and innovative approaches, farmers and agribusinesses can navigate the challenges of the future and ensure a thriving agricultural sector.
It’s a journey that requires adaptation, investment, and a commitment to continuous learning. The future of food security and environmental stewardship depends on our ability to use these trends in agriculture and shape a better world through agriculture.
FAQs
How Can Small-Scale Farmers Benefit From These Trends in Agriculture?
While some of these trends in agriculture may seem geared toward large-scale operations, many of them offer benefits to small-scale farmers as well. For example, digital agriculture tools can help smallholders optimize resource use and increase yields.
What is the Role of Government in Promoting These Trends in Agriculture?
Governments play a crucial role in fostering innovation and adoption of these trends in agriculture. This includes providing financial incentives, supporting research and development, and creating favorable regulatory environments. Additionally, policies that promote sustainable agriculture and food security are essential.
How Can Consumers Contribute to the Adoption of These Trends in Agriculture?
Consumers have a powerful role to play by supporting sustainable and ethically produced food. Choosing to buy local, organic, or sustainably sourced products can incentivize farmers to adopt these practices.
What are the Potential Challenges in Implementing These Trends in Agriculture?
The adoption of new technologies, practices, and agricultural trends can be challenging for farmers due to factors such as cost, access to technology, and education. Additionally, there may be uncertainties about the long-term impacts of some technologies, such as genetic engineering.
How Can We Ensure that the Benefits of These Trends in Agriculture are Distributed Equitably?
It is essential to address the potential disparities that may arise from the adoption of these trends in agriculture. Access to technology, education, and financial resources should be equitable to ensure that all farmers can benefit.
What is the Future Outlook for Agriculture?
The future of agriculture is bright, but it will require continued innovation and adaptation. By embracing the current trends in agriculture outlined in this blog, the agriculture industry can build a more sustainable, resilient, and productive food system that meets the needs of a growing population while protecting our planet.