By 2050, global food production is expected to increase by 70% to meet the needs of an estimated 9.7 billion people, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). That’s not just a number, it’s a wake-up call. With shrinking arable land, rising input costs, and climate unpredictability, farmers and agribusiness owners face unprecedented pressure to do more with less. This is where data in agriculture steps in, not as a luxury, but as a necessity.
Farming has always been a science of observation, watching the skies, reading the soil, and relying on intuition passed down through generations. But today, the stakes are higher, and the margin for error is thinner. We have shifted from observational practices to evidence-based, data-driven farming, where success hinges on decisions backed by facts, rather than guesswork.
This blog explores how data science in agriculture is transforming the field literally and how you can harness its potential to optimize your operations, cut costs, and boost agricultural productivity. Let’s explore how digging into the right data helps farmers of all sizes distinguish between real impact and empty promises.
What Is Data in Agriculture?
At its core, data in agriculture refers to the collection, analysis, and use of information to guide farming decisions. But it’s more than just numbers on a spreadsheet—it’s insights drawn from the land, livestock, and everything in between. Whether you’re managing 10 acres or 10,000, data helps you understand the conditions affecting your operation so you can act smarter, not harder.
Data in farming spans a wide range of categories, each playing a critical role in creating a comprehensive picture of what’s happening in the field, in real-time. These include:
- Environmental data – Weather conditions, temperature, rainfall patterns, and climate trends.
- Soil data – Nutrient levels, pH balance, moisture content, and compaction.
- Crop data – Plant growth stages, yield projections, disease presence, and harvesting times.
- Livestock data – Health records, breeding cycles, weight gain, and feed intake.
- Operational data – Labor hours, input usage (like fertilizers and pesticides), fuel consumption, and equipment efficiency.
- Market data – Commodity prices, supply chain trends, consumer demand, and trade forecasts.
- Equipment usage data – GPS tracking, machine health, maintenance schedules, and productivity metrics.
All these data points come together to form the foundation of data driven farming, where decisions are based on real-world evidence rather than guesswork.
Where Does This Data Come From?
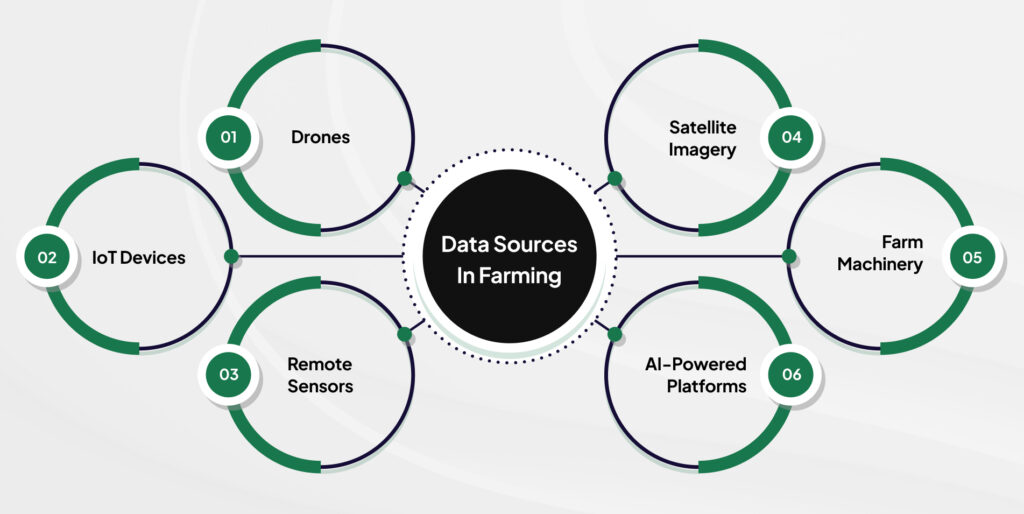
Today’s farms are more connected than ever. Data is collected through a range of smart technologies:
- Drones scan crops and map fields with precision.
- IoT (Internet of Things) devices measure soil moisture, temperature, and livestock activity.
- Remote sensors provide constant updates from the field.
- Satellite imagery tracks crop health and weather systems over time.
- Farm machinery now comes equipped with GPS and onboard computers that log every pass across the field.
- AI-powered platforms are helping process vast amounts of this data into meaningful insights.
Together, these tools contribute to data analytics in agriculture, providing actionable strategies to enhance productivity and profitability. With the right data management in agriculture, farmers can easily store, organize, and interpret this information to guide both their day-to-day tasks and long-term planning.
Key Technologies Driving Data in Agriculture
Modern farming is no longer just about tractors and tillers—it’s about tech. Behind every informed decision on the farm today, there’s a growing web of tools collecting, analyzing, and managing critical data. These technologies are the engine powering data driven farming, helping producers make smarter decisions, minimize waste, and improve yields.
Let’s explore the key technologies transforming how data in agriculture is gathered and used.
IoT and Sensors: The Eyes and Ears in the Field
According to MarketsandMarkets, the agricultural IoT market is projected to reach $18.1 billion by 2026, driven by the demand for precision and automation. On the ground, these appear to be sensors embedded in soil, attached to irrigation systems, or worn by livestock, all quietly collecting data 24/7.
IoT devices in agriculture measure a wide range of factors, including soil moisture, nutrient levels, weather patterns, and animal activity. This constant data collection in agriculture enables farmers to make informed decisions, such as when to irrigate or apply fertilizer, rather than relying on intuition. More importantly, it supports long-term strategies around data analysis in agriculture, enabling better planning for future seasons.
Drones and Remote Sensing: Real-Time Monitoring from Above
Drones in agriculture are doing more than capturing stunning aerial shots, they’re working in fields with unmatched efficiency. Equipped with multispectral cameras, drones deliver real-time insights on crop health using AI, pest issues, and field variability.
Combine that with remote sensing and satellite imagery, and farmers gain a bird’s-eye view of their operation literally. These tools contribute to data driven farming by identifying problems early, allowing for targeted interventions rather than blanket solutions.
The result? Healthier crops, lower input costs, and better yields.
AI and Machine Learning: Smarter Decisions, Even Offline
It’s not about robots taking over the farm, it’s about giving farmers better tools to work with. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning analyze complex datasets from the field and transform them into actionable insights. What was once a mountain of raw data becomes a clear path forward.
The best part? Some AI tools in agriculture are practical even in remote areas with limited or no internet access. For example, Folio3 AgTech offers specialized solutions for both crop and livestock management, each equipped with AI-driven features designed to support data-driven farming. In livestock operations, our Feedlot Management Software uses AI to detect early signs of illness, automate feed tracking, and optimize weight gain strategies helping reduce costs and improve animal health outcomes.
On the crop side, our tools enable real-time monitoring, yield prediction, and precision task management, providing farmers with better control over resources and harvest timing. These targeted solutions allow farmers to use the full potential of data in agriculture, without needing to navigate complex systems.
This practical application of data science in agriculture enables farmers to solve problems more efficiently, manage risks more effectively, and increase their profitability.
Farm Management Software: All Your Data in One Place
Managing a farm often means juggling countless spreadsheets, logs, and paper records. That’s where farm management software steps in. These platforms consolidate various data streams, including crop health, weather patterns, market prices, labor records, and other relevant data, into a single digital dashboard.
Folio3 AgTech offers dedicated solutions for both crop and livestock management, tailored to the unique needs of each operation. Our crop management software help farmers monitor field conditions, track inputs, and improve yield forecasting through real-time data analysis.
For livestock, tools like our Feedlot Management Software enable automated health tracking, feed optimization, and performance monitoring. For agribusinesses seeking deeper integration, Folio3 AgTech’s ERP solutions for agriculture provide a centralized system to manage crops, livestock, finances, inventory, and compliance, streamlining data management in agriculture and supporting scalable, data-driven growth.
And because many of these systems are cloud-based, farmers can access key insights from the field, office, or even their phone.
Blockchain: Transparency from Farm to Fork
While blockchain is often associated with cryptocurrency, its true power in agriculture lies in its ability to provide traceability. With more consumers demanding to know the origin of their food, blockchain in agriculture offers a secure and transparent way to track everything from seed to sale.
Every time a product moves along the supply chain, a record is logged. This enhances data analysis in agriculture by establishing a permanent audit trail, which is particularly valuable in organic or export-driven markets.
For farmers and agribusiness owners, this level of traceability can open doors to premium markets and mitigate risk in the event of recalls or disputes.
What’s Working on the Farm? – Data Applications That Are Paying Off on the Farm
The real power of data in agriculture lies in its practical application. Across farms, both big and small, data-backed strategies are addressing long-standing challenges like cutting costs, improving yields, and enabling farmers to plan with greater confidence. Let’s examine four areas where data driven farming is making a measurable difference.
Cutting Waste, Growing More – How Precision Ag Maximizes Every Acre?
Precision agriculture isn’t just about using tech—it’s about using the right data collection in agriculture to apply water, fertilizer, and pesticides only where they’re truly needed. Precision ag practices can reduce chemical use by up to 30% and increase yields by 15% or more, depending on the crop and conditions.
Field maps generated from drone footage and soil sensors help pinpoint variability across plots. With this approach, farmers spend less on inputs, reduce runoff, and support long-term soil health. It’s a practical win that showcases the role of data analytics in agriculture in achieving sustainability without sacrificing profit.
Smarter Herds Using Data to Predict and Prevent Livestock Issues
In livestock operations, data is shifting animal care from a reactive to a proactive approach. By tracking feed intake, weight gain, behavior, and temperature in real-time, farmers can detect health issues early, before they escalate into costly problems.
Tools like Folio3 AgTech’s Feedlot Management Software allow producers to monitor everything from vaccination schedules to feed efficiency. This type of data management in agriculture not only reduces mortality rates but also enhances overall productivity and animal welfare, which is crucial for meeting both market demand and regulatory standards.
Data-Driven Timing for Peak Yields
Harvesting too early or too late can result in both yield and quality losses for farmers. That’s where data science in agriculture steps in. Satellite imagery, crop modeling, and weather forecasting tools now help farmers pinpoint the ideal window for harvesting.
By syncing crop maturity data with weather trends, farmers can reduce spoilage, improve storage outcomes, and maximize market value—all made possible through smart data analysis in agriculture.
Optimizing Supply Chains with Real-Time Farm Data
Data driven farming doesn’t stop at the field. From harvest to market, logistics and inventory decisions are now guided by real-time data. Farmers can monitor transportation timing, track storage conditions, and forecast demand using farming software and online data in agricultural platforms.
With global supply chains still recovering from disruptions, such data driven farming tools are vital for risk mitigation, pricing accuracy, and building resilient operations that adapt quickly to change.
What’s Not Working? – Real-World Challenges Farmers Face
While the potential of data in agriculture is immense, many farmers still face obstacles that limit the return on their digital investments. These aren’t abstract tech issues, they’re everyday roadblocks that impact how practical, accessible, and actionable farm data is. Understanding these pain points is the first step toward building smarter, more farmer-friendly solutions.
Information Overload is Causing Decision Fatigue
Modern farms can generate thousands of data points a day, from moisture levels to market trends. But without the right tools to filter and interpret it all, this flood of information often creates more confusion than clarity. Farmers are left asking: Which data matters? This is where farming software and online data in agricultural platforms must evolve—offering clear, prioritized insights rather than raw numbers, helping farmers make faster, more confident decisions without being overwhelmed by dashboards.
Small and Mid-sized Farms Struggle to Adopt High-tech Tools
Many advanced tools in data-driven farming are tailored for large commercial operations, often leaving small and mid-size farms behind. Upfront costs, steep learning curves, and a lack of support slow adoption. To address this, tech providers must rethink their pricing, establish local support channels, and offer scalable solutions that evolve with the farm. Technology providers like Folio3 AgTech are beginning to bridge this gap by providing modular, easy-to-use tools that don’t require an IT background to operate.
Infrastructure Gaps, Like Rural Connectivity & Power Supply Challenges
A digital platform is only as reliable as the internet or power source supporting it. In many rural regions, poor connectivity continues to disrupt data collection in agriculture, particularly during peak farming seasons. This makes it difficult to rely on real-time updates and cloud-based tools. Offline-friendly software, low-bandwidth solutions, and hybrid sync capabilities are now essential to ensure consistent data access in the field, especially in areas where infrastructure remains patchy.
Tools That Don’t Match Real Farm Life
Not all tech was built with farming in mind. Generic systems can feel out of touch, offering features that look good on paper but don’t solve practical, on-the-ground problems. This often results in wasted time and frustration. Tools designed by ag-specialized teams—who understand cropping cycles, livestock management, and local conditions can significantly enhance data management in agriculture and help farmers derive real value from their technology investments.
Who’s In Control of Your Farm Data?
As more operations turn digital, a growing concern is: Who owns the data? Farmers generate it, but too often third-party platforms hold the keys. This raises questions about privacy, control, and even competitive exposure. Clear, farmer-first policies must be implemented—here, farmers retain full ownership and have control over how their data is used, shared, or monetized. Trust, after all, is the foundation of any good data-driven relationship.
Debunking Common Myths About Farm Data
Despite the growing success stories around data in agriculture, some myths continue to hold farmers back from fully embracing its potential. Let’s break down these common misconceptions and explain why the truth is often more practical than hype.
Myth 1: More Data Always Means Better Decisions
Collecting more numbers automatically leads to more intelligent choices. But in reality, too much data without context can lead to decision fatigue and inaction. What matters most isn’t the quantity, it’s data analysis in agriculture that filters the noise and delivers relevant, actionable insights. The best systems don’t overwhelm; they simplify.
Myth 2: Data Replaces Farmer Intuition
Good data doesn’t replace your experience, it complements it. Data-driven farming adds a layer of evidence to support your gut instincts. Whether it’s deciding when to irrigate, rotate crops, or change feed strategies, data helps confirm what you suspect and flag what you might miss. It’s not about replacing the farmer, it’s about strengthening decision-making with a reliable second opinion.
Myth 3: Data Systems Are Only for Big Farms
This is one of the most significant barriers to the adoption of data science in the agricultural sector. While large-scale operations were early adopters, today’s farming software and online data in agriculture tools are built to serve farms of all sizes. With scalable pricing, mobile access, and modular features, even smaller farms can benefit from tools that enhance yields, minimize waste, and track performance without incurring significant costs.
Myth 4: Tech Will Solve Every Farming Problem
Even the most advanced system won’t address poor soil, unpredictable markets, or outdated practices. Technology is a tool, not a cure-all. What it does offer is better visibility, faster responses, and fewer surprises. When used effectively, data analytics in agriculture can help prioritize actions, mitigate risks, and uncover opportunities that might have otherwise gone unnoticed. But real change still depends on good farm management, sound agronomic practices, and the person behind the screen.
Conclusion
Data in agriculture is transforming how farms operate, improving yields, reducing waste, and driving more intelligent decisions. But without the right tools, it can also lead to overwhelm, poor adoption, and missed opportunities. That’s why Folio3 AgTech offers a tailored farm management platform designed for real-world farming.
From precision crop tracking to livestock and feedlot monitoring, Folio3 AgTech turns complex data into clear, actionable insights. Whether you manage a small farm or a large agribusiness, it’s time to make data work for you.
Talk to the experts at Folio3 AgTech and grow smarter.
FAQs
What Is The Meaning Of Data-Driven Farming?
Using real-time farm data to make informed decisions that improve productivity, efficiency, and sustainability
What Is Database Farming?
It refers to storing and managing agricultural data in structured systems to support planning and operations.
What Is A Data-Driven Example In Farming?
Using soil sensor data to adjust irrigation schedules and optimize water usage.
What Are Data-Driven Farming Methods?
Techniques that rely on data analysis and insights rather than guesswork to guide farming decisions.