Data has become the new fertilizer in modern agriculture, powering a revolution changing how food is grown, managed, and distributed. As global challenges like climate change, food security, and resource scarcity intensify, the need for innovative solutions in agriculture has never been more urgent.
Data analytics is stepping in as a game-changer, offering farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers powerful tools to make informed decisions that boost yields, reduce costs, and drive sustainability.
Keep reading this blog to explore the transformative impact of data analytics on agriculture.
The Role of Data Analytics in Modern Agriculture
Data analytics is not just a tool for improving agricultural practices—it is necessary to ensure the future of global food security. With the power of data, the agriculture industry can become more resilient, sustainable, and capable of feeding the world’s growing population.
Defining Data Analytics in Agriculture
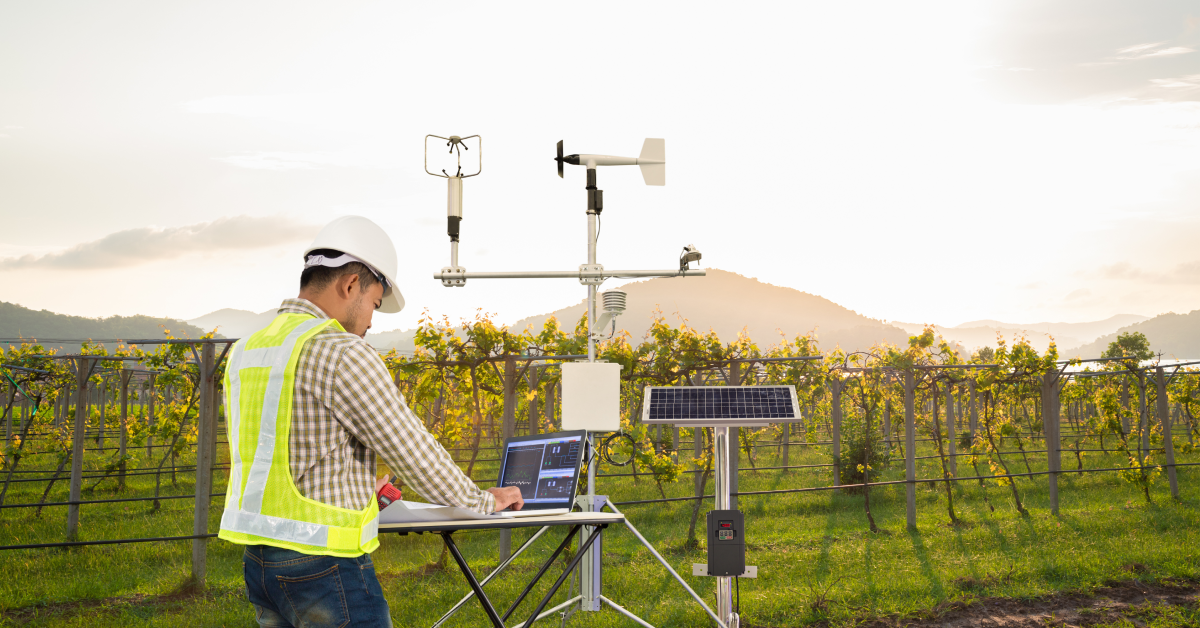
Data analytics in agriculture involves collecting, processing, and analyzing vast amounts of data to drive decision-making and optimize farming practices. This data can come from a variety of sources, including:
- Weather Patterns: Monitoring temperature, humidity, rainfall, and other climatic factors to predict how crops perform under different conditions.
- Soil Health: Collect soil composition, moisture levels, and nutrient content data to determine the best crops to plant and the most effective fertilizers.
- Crop Yields: Analyzing historical and real-time data on crop performance to forecast yields and optimize harvesting schedules.
- Farm Equipment: Utilizing data from sensors and IoT devices on tractors, irrigation systems, and other machinery to enhance operational efficiency.
- Market Trends: Gathering data on commodity prices, demand fluctuations, and consumer preferences to make informed decisions about planting and selling.
Historical Context
Data has always been important in all types of agriculture, but its application has evolved significantly. Traditionally, farmers relied on experience and observations passed down through generations to guide their practices.
Simple records of rainfall, crop yields, and market prices helped them plan their activities and manage risks. However, modern technology has revolutionized how agriculture collects, processes, and utilizes data.
With the development of GPS technology, remote sensing, and advanced software, farmers can now gather precise data on nearly every aspect of their operations.
These advancements have turned agriculture into a data-driven industry, where decisions are no longer based solely on intuition but on robust analytical insights that can significantly enhance productivity and sustainability.
Why Data Analytics Matters?
The agriculture industry is under increasing pressure to meet the demands of a growing global population while also addressing environmental sustainability. By 2050, the world’s population is expected to reach nearly 10 billion, which will require a 60-70% increase in food production.
At the same time, farmers must contend with the effects of climate change, such as unpredictable weather patterns, water scarcity, and soil degradation, all of which threaten agricultural productivity. Data analytics in agriculture offers robust solutions to these challenges by enabling farmers to optimize their use of resources, reduce waste, and increase crop yields.
For example, precision farming techniques use data to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides in the exact amounts needed, minimizing environmental impact while maximizing efficiency. Predictive analytics can help farmers anticipate and mitigate risks such as pest infestations or extreme weather events, ensuring more stable and reliable food production.
Key Applications of Data Analytics in Agriculture
Below are the critical applications of data analytics in agriculture that can ensure a more resilient and efficient agricultural system for the future.
Precision Farming
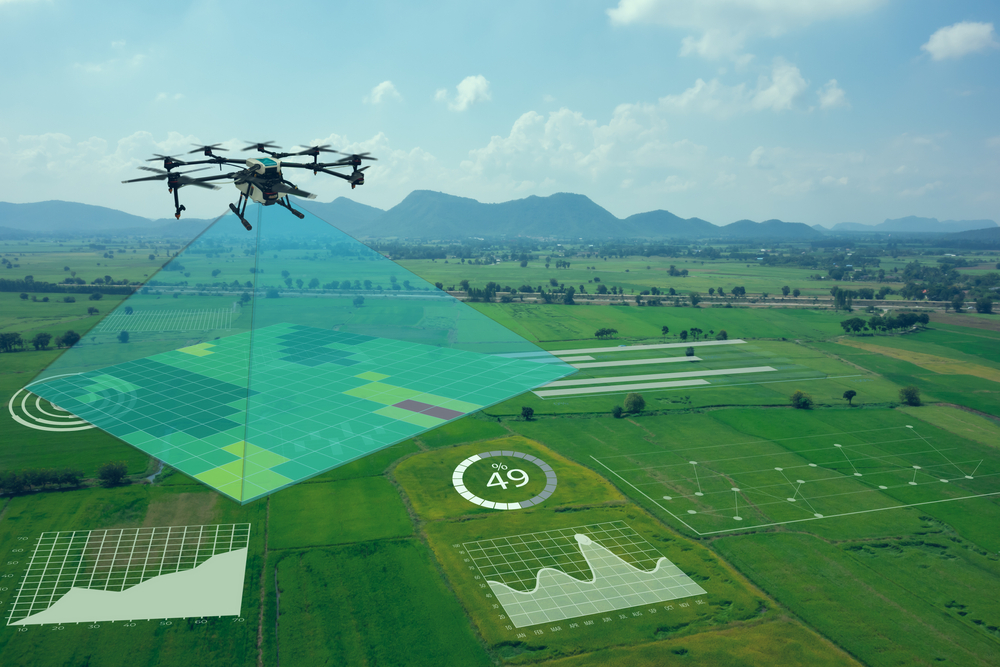

Precision farming, or precision agriculture, involves using data analytics to make farming practices more efficient and effective.
Farmers can precisely manage resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides using data from various sources, ensuring they are applied in the right amounts at the correct times. This approach maximizes crop yields and minimizes waste and environmental impact.
How Data Analytics Enables Precision Farming?
Data analytics allows farmers to analyze information from soil sensors, weather stations, and satellite imagery to determine the specific needs of different areas within a field. For example, sensors can measure soil moisture levels, enabling farmers to irrigate only those parts of the field that need water, reducing water usage and preventing overwatering.
Examples of Precision Farming Technologies
- Sensors: Soil and crop sensors provide real-time data on moisture levels, nutrient content, and plant health, enabling farmers to make precise adjustments.
- Drones: Drones in agriculture equipped with cameras and sensors can capture detailed aerial images of fields, helping farmers monitor crop conditions, detect pest infestations, and assess plant health.
- GPS-guided Equipment: Tractors and other machinery equipped with GPS technology can follow precise paths, ensuring even distribution of seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs.
Predictive Analytics
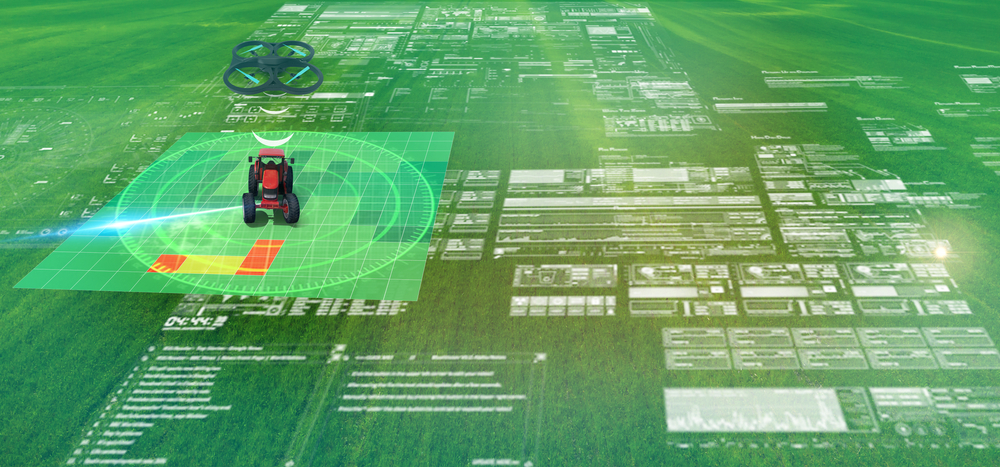

Predictive analytics involves using historical data to forecast future outcomes, helping farmers anticipate and prepare for challenges such as weather changes, pest infestations, and variations in crop performance.
How Predictive Analytics Help Farmers?
Predictive models can analyze past data on weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop yields to provide farmers with insights into when to plant, irrigate, and harvest the most profitable crops.
For instance, if historical data indicates that a specific region will likely experience a dry spell during a certain period, farmers can adjust their irrigation schedules accordingly to protect their crops.
Examples of Predictive Analytics in Agriculture
- Weather Forecasting: Advanced models use historical weather data to predict future climate conditions, enabling farmers to take proactive measures.
- Pest and Disease Prediction: Predictive analytics can help farmers identify potential threats early and take preventive actions by analyzing data on past pest outbreaks.
- Yield Forecasting: Predictive models can estimate crop yields based on historical data, helping farmers plan their harvests and manage supply chain logistics.
Supply Chain Optimization
Data analytics is crucial in optimizing the agricultural supply chain, from farm to market. Farmers and agribusinesses can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and ensure that products reach consumers optimally by analyzing production, transportation, and consumer demand data.
Role of Data in Reducing Waste
Data analytics enables real-time tracking of products throughout the supply chain, helping to identify inefficiencies and areas where waste can be reduced. For example, data can be used to optimize harvest times using a modern harvest management software, to ensure that produce reaches the market at its peak freshness, reducing spoilage.
Impact of Real-Time Tracking
Real-time data on transportation routes, storage conditions, and market demand allows farmers and distributors to decide where and when to send their products. This helps ensure that agricultural products are distributed efficiently, meeting market demand and minimizing food waste.
Sustainability and Resource Management
Data analytics is a powerful tool for promoting sustainable farming practices by optimizing resources such as water, energy, and fertilizers. By carefully managing these inputs, farmers can reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining or even improving productivity.
How does Data Analytics in Agriculture Contribute to Sustainability?
Data-driven practices enable farmers to use resources more efficiently, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. For instance, precision irrigation systems use real-time data to apply water only where and when needed, conserving water and preventing runoff that can lead to soil erosion and nutrient depletion.
Case Studies in Sustainability
- Water Conservation: A study in California found that data-driven irrigation systems reduced water usage by up to 30% while maintaining crop yields, demonstrating the potential for significant environmental benefits.
- Energy Efficiency: Data analytics in agriculture has been used to optimize the operation of farm machinery, reducing fuel consumption and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- Soil Health Management: By analyzing soil data, farmers can apply the right amount of fertilizer to specific areas of their fields, reducing the risk of nutrient runoff and improving soil health over time.
Benefits of Data Analytics for Farmers
Data analytics offer farmers:
- Improved Crop Yields: Data analytics in agriculture enables farmers to optimize planting schedules, manage soil health, and precisely monitor crops. Farmers can make informed decisions leading to higher yields and more efficient resource use by analyzing weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop performance data.
- Cost Reduction: Data-driven decisions allow farmers to allocate resources more effectively, reducing waste and lowering costs. For example, precision farming techniques minimize water use, fertilizers, and pesticides, significantly saving input costs and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data analytics in agriculture empowers farmers with actionable insights, enabling better strategic planning and risk management. Farmers can make smarter decisions about crop rotation, harvesting, and market timing by understanding trends and patterns, improving their long-term success.
- Risk Mitigation: Through predictive analytics, farmers can anticipate and mitigate risks related to climate change, pests, and market fluctuations. Farmers can proactively protect their crops and stabilize their income by using historical data to forecast potential challenges.
Challenges and Limitations of Data Analytics in Agriculture
Following challenges and limitations are encountered using Data Analytics in Agriculture:
Data Collection and Integration
One of the primary challenges in agricultural data analytics is collecting accurate and consistent data, particularly for small-scale farmers.
Factors like fragmented land holdings, lack of access to advanced tools, and varying levels of technical expertise can hinder effective data collection. Integrating data from diverse sources such as sensors, satellites, and manual records into a cohesive system is complex and time-consuming. Farmers can benefit from learning how to scan QR code on iPhone to quickly access data, track resources, and streamline record-keeping.
Data Quality and Accuracy
The effectiveness of data analytics in agriculture relies heavily on the quality and accuracy of the data used. Data can be prone to inconsistencies in agriculture due to sensor malfunctions, environmental variability, and human error during data entry.
High-quality data is essential for producing reliable insights, but achieving this can be challenging, especially in dynamic field conditions.
Cost and Accessibility
The financial barriers to adopting data analytics tools can be significant, particularly for smaller farms. Advanced technologies like drones, IoT sensors, and specialized software often require substantial upfront investment, which may only be feasible for some farmers. According to ScienceSoft, data analytics services may cost anywhere from $10,000 to over $1,000,000, depending on factors like data complexity, real-time versus batch processing, and the use of AI or big data technologies. For smaller agricultural operations, focusing on specific use cases such as yield forecasting or precision irrigation can help reduce costs while still gaining valuable insights.
Additionally, ongoing data storage, processing, and technical support costs can add to the burden, limiting accessibility for those with limited resources.
Data Privacy and Security
As data becomes increasingly central to agricultural operations, concerns about data ownership, privacy, and security are growing. Implementing the best DSPM tools can help identify sensitive data across distributed systems, enforce access controls, and maintain compliance with evolving data governance standards. Farmers may need help with who can access their data and how it might be used, particularly if it is shared with third parties such as technology providers or agribusinesses.
Emerging Trends in Agricultural Data Analytics
Agricultural data analytics is rapidly evolving, introducing new technologies that are reshaping how we farm. As these innovations gain traction, they promise to enhance efficiency, improve crop resilience, and meet the growing demands of a changing world.
Below are the emerging agricultural trends that are setting the stage for more innovative, more sustainable agriculture:
Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Farming
IoT devices are revolutionizing agriculture by enabling real-time data collection from various sources, including soil sensors, weather stations, and farm machinery.
These devices seamlessly integrate with data analytics platforms, providing farmers with a continuous stream of information that can be used to monitor crop health, optimize resource use, and automate farming processes. The result is more brilliant, efficient farming practices that can adapt to changing conditions in real-time.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning and AI are increasingly being employed to analyze complex agricultural datasets, uncovering patterns and trends that might be invisible to the human eye.
These technologies can predict crop yields, detect diseases early, and optimize planting schedules by processing vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. AI-driven agricultural tools empower farmers with actionable insights that enhance decision-making and boost productivity.
Blockchain for Data Transparency
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in agriculture because it can ensure transparency and traceability in the supply chain.
By recording every transaction and movement of agricultural products on a blockchain, farmers and consumers can have confidence in the authenticity and quality of food products.
This technology also helps verify producers’ sustainability practices, making the agricultural process more transparent and trustworthy.
Sustainability and Climate Resilience
With climate change posing significant risks to agriculture, emerging trends focus on using data analytics in agriculture to build climate-resilient farming practices.
Farmers can adopt strategies that minimize environmental impact while maximizing resilience to extreme weather events by analyzing climate data, soil health, and crop performance.
Data-driven approaches are helping to create more sustainable agricultural systems that can adapt to the challenges posed by a changing climate.
The Future of Data Analytics in Agriculture
The future of data analytics in agriculture promises to transform farming by making advanced technologies accessible to farms of all sizes. As data analytics integrates with innovations like drones, robotics, and sensors, farms will become more innovative and efficient.
With supportive policies and regulations, the widespread adoption of these technologies will drive sustainability and productivity in agriculture. However, here’s what we can expect:
Scaling Data Analytics in Agriculture
As technology advances and becomes more affordable, we can expect data analytics to be more widely adopted across farms of all sizes.
Innovations in user-friendly software and cost-effective hardware solutions will make it easier for small and medium-sized farms to use the power of data analytics in agriculture.
Integration with Other Technologies
The future of agriculture will likely see a seamless integration of data analytics with other emerging technologies such as drones, robotics, and advanced sensors.
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors will provide detailed aerial data, which, when analyzed, can guide autonomous robots to perform tasks like planting, weeding, and harvesting with precision.
Advanced sensors will continue to enhance real-time monitoring of soil health, weather conditions, and crop growth, feeding this data into powerful analytics platforms that provide actionable recommendations to farmers.
Policy and Regulation
Government and industry regulations will play a crucial role in shaping the future of data analytics in agriculture. As data becomes more integral to farming operations, policies must address data privacy, ownership, and sharing issues.
Governments may also introduce incentives or subsidies to encourage the adoption of data-driven technologies, especially in regions where agriculture is a significant economic driver.
These regulatory frameworks will be essential in ensuring that the benefits of data analytics are realized while protecting the rights and interests of farmers and consumers alike.
Conclusion
Data analytics is revolutionizing agriculture, providing farmers with the tools to optimize resources, increase yields, and ensure sustainability in a rapidly changing world. As this technology continues to evolve, its integration with other advanced innovations will transform farming practices globally.
However, to fully exploit the potential of data-driven agriculture, challenges like data accessibility, quality, and privacy must be addressed. By implementing these technologies and addressing the associated challenges, the agriculture industry can meet the future’s growing demands while protecting the environment and enhancing food security.
FAQs
What is the role of data analytics in modern agriculture?
Data analytics in modern agriculture are crucial in optimizing farming practices, improving crop yields, and promoting sustainability. By analyzing data from various sources, such as weather patterns, soil health, and crop performance, farmers can make informed decisions that reduce costs, enhance productivity, and minimize environmental impact.
What challenges do farmers face when implementing data analytics in agriculture?
When implementing data analytics in agriculture, farmers face challenges like data collection and integration, data quality and accuracy, and the high cost of advanced tools. Ensuring consistent and accurate data collection, managing technology expenses, and addressing data privacy concerns are key hurdles that need to be overcome.
What are the emerging trends in agricultural data analytics?
Emerging trends in agricultural data analytics include the adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning and AI, and blockchain integration for data transparency. These technologies are revolutionizing how farmers monitor crop health, optimize resources, and ensure transparency throughout the supply chain.
What challenges do farmers face when implementing data analytics in agriculture?
When implementing data analytics in agriculture, farmers face challenges like data collection and integration, data quality and accuracy, and the high cost of advanced tools. Ensuring consistent and accurate data collection, managing technology expenses, and addressing data privacy concerns are key hurdles that need to be overcome.





