The Ovum Pick-Up (OPU) technique has become a foundational tool in modern livestock breeding, particularly in cattle, where improving reproductive efficiency and accelerating genetic progress are ongoing priorities. Recent peer-reviewed research shows that repeated OPU combined with in vitro embryo production can substantially increase the number of embryos produced compared to conventional embryo transfer, reinforcing its growing role in commercial and structured breeding programs. By enabling more frequent and efficient oocyte collection from elite donor females, OPU has reshaped how breeders approach genetic advancement, conservation, and reproductive planning.
In this blog, you will learn how the Ovum pick-up technique works step by step, why it has become important in modern animal breeding, its key applications and advantages in livestock management, the challenges associated with its adoption, and how OPU is expected to shape the future of global livestock production.
Importance of OPU in Modern Animal Breeding
Ovum pick-up is instrumental in accelerating genetic progress, preserving endangered breeds, and optimizing livestock reproduction. It has revolutionized the livestock industry by enabling the production of high-quality embryos and improving overall herd genetics.
What is Ovum Pick-Up (OPU)
Ovum Pick-Up (OPU) is a technique for collecting egg cells from the ovaries of female livestock. These oocytes can then be fertilized in vitro to produce embryos, which can be either cryopreserved or transferred to recipient females.
Purpose and Benefits of OPU in Livestock Breeding
The primary purpose of OPU is to enhance reproductive efficiency and genetic diversity in livestock. It allows breeders to harvest multiple oocytes from valuable females, maximizing their genetic contribution and enabling the production of embryos for commercial or conservation purposes.
This results in significant benefits for livestock breeding, including accelerated genetic progress and the preservation of endangered breeds.
The Ovum Pick-Up Process
The Ovum Pick-Up (OPU) process is a sophisticated and delicate procedure central to modern livestock breeding techniques. It involves the precise extraction of oocytes, or egg cells, from the ovaries of donor animals, which can then be fertilized and developed into embryos.
This process maximizes the genetic potential of valuable females and enables breeders to optimize reproductive outcomes and accelerate genetic improvement within a herd. Here’s how the Ovum process works:
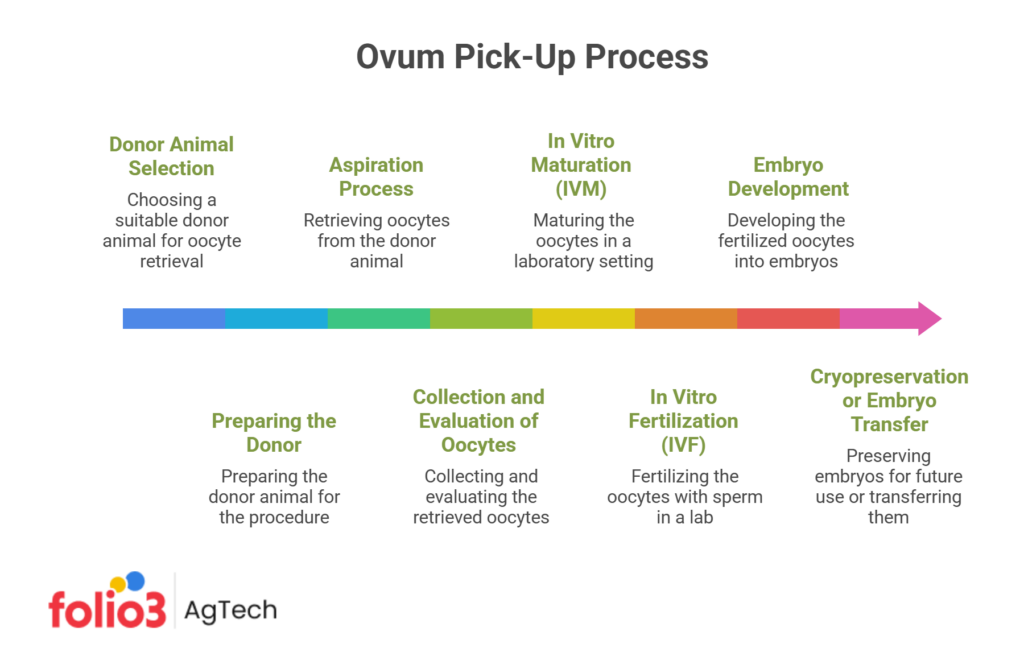
Donor Animal Selection
Selecting suitable donor animals is crucial for the success of Ovum Pick-Up. Donor females are chosen based on their genetic merit, health, age, and reproductive history. These animals typically possess desirable traits that breeders wish to propagate.
Preparing the Donor
Before the Ovum Pick-Up procedure, donor animals undergo hormonal treatment to stimulate the development of multiple follicles on their ovaries. This process, known as superovulation, increases the number of oocytes available for collection.
Aspiration Process
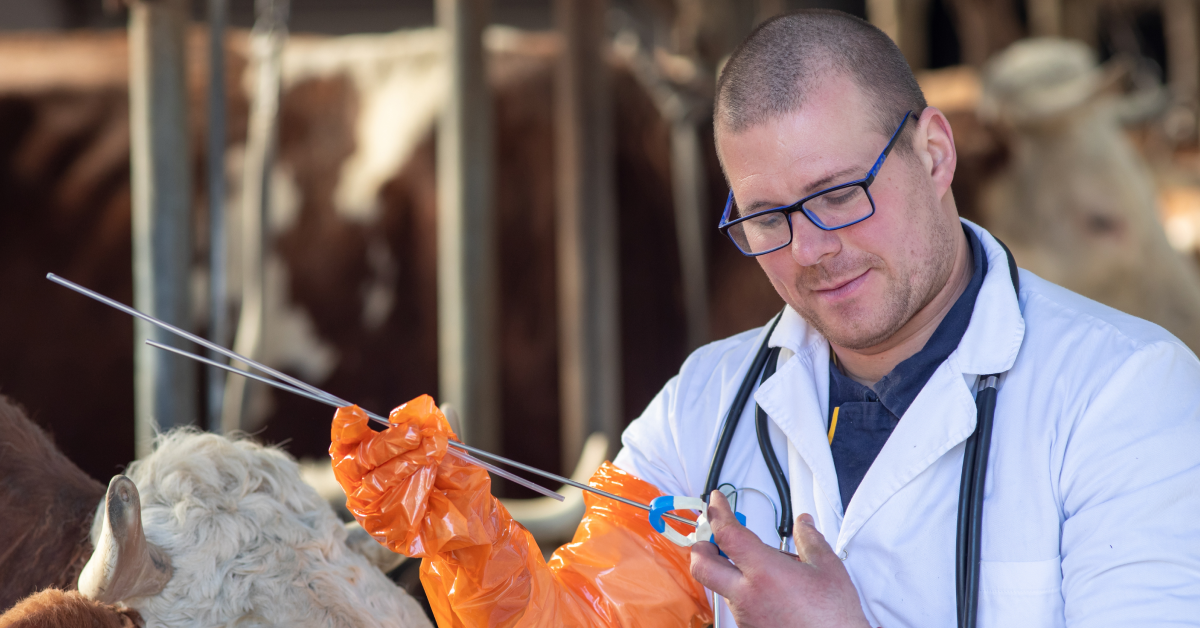
The Ovum Pick-Up procedure begins with the donor animal being anesthetized. An ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum to visualize the ovaries. A needle is then guided through the vaginal wall into the follicles, where the oocytes are gently aspirated.
Collection and Evaluation of Oocytes
The aspirated fluid, containing the oocytes, is collected in a sterile tube and examined under a microscope. Only viable oocytes are selected for further processing, ensuring the best chances for successful fertilization and embryo development.
In Vitro Maturation (IVM)
The selected oocytes undergo in vitro maturation (IVM) in a specialized medium. This step is crucial as it prepares the oocytes for fertilization, enhancing their developmental potential.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
The next step is in vitro fertilization (IVF), where the mature oocytes are fertilized with sperm outside the animal’s body. This process is integral to Ovum Pick-Up and allows for controlled breeding and genetic manipulation.
Embryo Development
Following fertilization, the embryos are cultured until they reach a specific developmental stage, typically the blastocyst stage, which occurs around seven days after fertilization.
Cryopreservation or Embryo Transfer
The developed embryos can either be cryopreserved for future use or transferred immediately to recipient females. Cryopreservation offers flexibility in timing, making it a valuable tool for managing breeding programs.
Applications of Ovum Pick-Up in Livestock Management
The application of Ovum Pick-Up (OPU) in livestock management has expanded significantly as breeding programs seek greater control, predictability, and efficiency. Beyond its technical role, OPU supports structured decision-making across genetics, reproduction, and long-term herd planning.
Accelerating Genetic Progress
Ovum Pick-Up is not just a tool but a catalyst for rapid genetic improvement. It enables the multiplication of DNA from superior females, allowing breeders to accelerate genetic progress within a herd rather than waiting for natural reproductive cycles. This capability plays a central role in modern livestock breeding, where shortening generation intervals and increasing the influence of elite animals are key objectives.
By producing more embryos from genetically superior donors, OPU helps operations align breeding outcomes with clearly defined performance goals, whether related to productivity, adaptability, or disease resistance.
Protection of Endangered Breeds
The technique is vital for conserving endangered breeds and safeguarding genetic diversity. OPU allows valuable genetic traits to be preserved and propagated even when population numbers are low or natural reproduction is limited. In conservation-focused programs, this capability supports responsible genetic stewardship while ensuring rare traits are not lost over time.
When combined with structured data collection and analysis, OPU also contributes to broader initiatives such as precision livestock farming, where genetic information is used alongside performance data to guide sustainable breeding strategies.
Optimized and Efficient Reproduction
OPU is particularly beneficial for animals with reproductive challenges, including those unable to conceive or carry pregnancies naturally. By extracting oocytes directly from donor females, breeding programs can continue utilizing valuable genetics that might otherwise be excluded.
This approach improves overall reproductive efficiency and reduces dependency on conventional breeding timelines, giving operations greater flexibility in managing donor and recipient programs.
Embryo Production for Financial Gain
The commercial production of embryos through OPU and IVF has become an established revenue stream for many breeding operations. High-quality embryos produced from elite donors can be marketed to meet demand from domestic and international buyers.
From a business perspective, this creates opportunities for structured livestock financial planning, where breeding investments, production costs, and genetic returns can be evaluated more accurately over time.
Exams and Genetic Studies
OPU is a valuable tool for research and genetic studies, enabling scientists and breeding organizations to study specific traits, gene functions, and reproductive biology in detail. Controlled oocyte collection allows for targeted experimentation and evaluation without relying on natural breeding variability.
These studies contribute to advancements in breeding efficiency, animal health, and long-term productivity across livestock systems.
Advantages of the OPU Method
The advantages of the OPU method extend beyond increased embryo production and touch multiple aspects of herd management and planning.
Increased Genetic Profit
By allowing multiple oocyte harvests from valuable females, OPU maximizes genetic profit and increases the return on elite genetics. This makes it a highly effective tool for operations focused on long-term genetic improvement.
Extended Reproductive Lifespan
OPU extends the reproductive lifespan of females by enabling oocyte extraction even after natural reproductive performance has declined. This allows breeders to continue benefiting from proven genetics beyond traditional breeding limits.
More Adaptability in Reproductive Initiatives
The ability to cryopreserve embryos provides flexibility in timing and resource allocation. Breeders can adjust transfer schedules, manage recipient availability, and respond to market conditions more effectively when embryos are stored and tracked digitally.
Challenges and Impediments of OPU
While the Ovum Pick-Up technique offers clear advantages, it also presents challenges that must be evaluated carefully. Successful implementation depends on technical expertise, ethical oversight, and financial feasibility.
Need for Expert Technicians
The OPU process requires skilled technicians, precise equipment, and controlled laboratory conditions. Limited access to trained personnel can restrict adoption, particularly for smaller or remote operations.
Welfare of Donor Animals
Animal welfare is a critical consideration. Proper handling, sedation, recovery protocols, and monitoring are essential to ensure donor animals remain healthy throughout repeated OPU procedures.
Cost Considerations
The costs associated with OPU include hormonal treatments, equipment, laboratory processes, and skilled labor. Without proper systems in place to digitize livestock record keeping, it can be difficult for operations to fully understand the true cost and return of OPU programs.
Future Perspectives of OPU in Livestock Breeding
The future of Ovum Pick-Up in livestock breeding points toward greater efficiency, wider adoption, and deeper integration with digital systems.
Potential Advancements and Innovations in OPU
As reproductive technologies advance, OPU is expected to achieve higher success rates with reduced stress on animals and lower operational costs. Improvements in imaging, automation, and data integration will further enhance its applicability across species.
Technology Integration in Modern OPU Programs
As OPU programs expand, managing donor data, lab workflows, embryo inventories, and compliance requirements becomes increasingly complex. Purpose-built cattle IVF software supports this transition by centralizing reproductive data, automating protocol tracking, and maintaining complete histories across OPU, IVF, and embryo transfer cycles.
By connecting field activity with laboratory outcomes, technology enables breeding programs to move beyond manual tracking and improve transparency, traceability, and operational efficiency. This digital layer is becoming essential for scaling OPU programs without increasing administrative burden or risk.
Role of OPU in Global Livestock Production
OPU will continue to play a crucial role in global livestock production by supporting genetic improvement, conservation efforts, and sustainable breeding practices. When paired with accurate data management and strategic planning, OPU enables operations to scale responsibly while maintaining control over genetic outcomes.
Conclusion
Ovum Pick-Up (OPU) has established itself as a transformative technique in livestock breeding by enabling greater control over genetic advancement, reproductive efficiency, and long-term herd development. By allowing repeated access to elite genetics, OPU supports breeding programs that aim to accelerate progress while maintaining consistency and traceability across production cycles.
While the technique requires technical expertise, careful animal welfare management, and financial planning, its benefits continue to outweigh these challenges for structured and forward-looking operations. As breeding programs grow more data-driven and interconnected, OPU fits naturally into modern livestock systems that prioritize accuracy, sustainability, and informed decision-making.
Looking ahead, continued innovation in reproductive technologies and digital management tools will further strengthen the role of OPU in global livestock production. Its ability to support genetic improvement, conservation efforts, and scalable breeding strategies ensures it will remain a cornerstone of modern animal breeding for years to come.
FAQs
What Is The Ovum Pick-Up Procedure?
The ovum pick-up procedure is a reproductive technique used to collect oocytes from the ovaries of live donor animals. It is performed using ultrasound guidance, where a probe allows visualization of the ovaries and a needle aspirates oocytes from individual follicles. The collected oocytes are then matured and fertilized in vitro to produce embryos for transfer or cryopreservation.
How Long Does Ovum Pick-Up Take?
An ovum pick-up session typically takes between 20 and 40 minutes per donor animal. The exact duration depends on factors such as the number of follicles present, the animal’s anatomy, and the experience of the technician. Preparation and recovery time may extend the overall handling period, but the aspiration itself is relatively brief.
Is Ovum Pick-Up Painful For Cattle?
When performed correctly by trained professionals, ovum pick-up is generally well tolerated by cattle. The procedure is conducted under appropriate sedation and pain management protocols to minimize discomfort. Proper handling, technique, and post-procedure care are essential to ensure animal welfare and reduce stress.
What Is The Success Rate Of OPU?
The success rate of OPU varies based on factors such as donor genetics, age, health status, laboratory conditions, and operator expertise. While oocyte recovery rates and embryo development outcomes differ between programs, well-managed OPU IVF systems consistently produce viable embryos and are widely used in commercial and conservation breeding programs.





