Agriculture stands at a pivotal crossroads, balancing the imperative to feed a growing global population with the need to preserve our planet’s health. The urgency for 7 sustainable agriculture practices has never been more pronounced. The World Wildlife Fund emphasizes that as the world’s population grows, the demand for agricultural commodities is rising rapidly, making sustainable resource management increasingly urgent.
The global sustainable agriculture market is projected to grow from $15.07 billion in 2024 to $16.75 billion in 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.2%. This growth underscores the escalating commitment to sustainable farming methods.
For farmers, agribusinesses, food producers, and agricultural researchers, adopting 7 sustainable agriculture practices is not merely an environmental consideration but also a strategic economic decision. Implementing environmentally friendly 7 sustainable agriculture practices can enhance soil health, increase biodiversity, and improve crop resilience, ensuring long-term productivity and profitability.
Let’s explore 7 sustainable agriculture practices. These 7 sustainable agriculture practices not only exemplify sustainable farming techniques but also offer practical solutions to the challenges faced by modern agriculture.
Why Sustainable Agriculture is Essential in Today’s Farming?
Sustainable agriculture is no longer an option—it’s a necessity. With the global population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, the demand for food is expected to increase by 60%. However, conventional farming methods limit natural resources, leading to soil degradation, water scarcity, and biodiversity loss. Implementing 7 sustainable agriculture practices is critical for ensuring food security while preserving ecosystems for future generations. These practices also align with the EUDR (European Union Deforestation Regulation), helping businesses ensure their agricultural products are deforestation-free and fully traceable.
Addressing Climate Change and Environmental Degradation
The global population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, leading to an anticipated 60% increase in food demand. Sustainable farming methods, such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and regenerative farming, help sequester carbon, reduce emissions, and improve soil health, making agriculture more resilient to climate change.
Improving Soil and Water Health
Traditional farming depletes soil nutrients, leading to erosion and reduced crop yields. Over 33% of the world’s soils are degraded due to unsustainable practices. Sustainable agricultural methods—cover cropping, conservation tillage, and organic composting—restore soil fertility and enhance water retention. Precision irrigation and rainwater harvesting also conserve water resources, ensuring long-term productivity.
Enhancing Economic Viability for Farmers
While the upfront costs of transitioning to sustainable farming may seem high, the long-term benefits outweigh them. Studies show that farmers who adopt environmentally friendly practices of sustainable agriculture experience lower input costs, increased yields, and better market opportunities. Consumers increasingly demand organic and sustainably produced food, driving higher profits for businesses prioritizing sustainability.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Balance
Monocropping and chemical-intensive agriculture have led to a drastic decline in pollinators and beneficial microorganisms. 7 sustainable agriculture practices, such as integrated pest management (IPM) and polyculture farming, encourage biodiversity, reducing the need for synthetic pesticides while maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Ensuring Food Security for Future Generations
Implementing sustainable farming techniques allows farmers to produce food efficiently without compromising future agricultural productivity. Agroecological farming, permaculture, and agroforestry are excellent examples of sustainable agriculture that maintain high yields while protecting natural resources.
The Best 7 Sustainable Agriculture Practices
7 sustainable agriculture practices help farmers maintain soil health, conserve water, and reduce environmental impact while ensuring long-term productivity. Below, we explore seven key methods of sustainable agriculture that exemplify environmentally friendly agricultural practices.

1. Crop Rotation and Diversity
Crop rotation involves alternating crops in the same field over seasons to prevent soil depletion and enhance biodiversity. It is one of the most effective 7 sustainable agriculture practices, reducing the overuse of specific soil nutrients and lowering the need for synthetic fertilizers.
How It Prevents Soil Depletion and Pest Buildup
Continuous monocropping depletes soil nutrients and creates an ideal environment for pests and diseases. Rotating crops, such as planting legumes after cereal crops, replenishes essential nutrients like nitrogen. This reduces the reliance on chemical fertilizers while breaking pest and disease cycles, leading to healthier crops and improved yields.
2. Cover Cropping
Cover crops are plants grown primarily to improve soil health rather than for harvest. These crops, such as rye, clover, and alfalfa, are planted between main cropping seasons to cover bare soil, preventing erosion and enhancing nutrient content.
How does It Prevents Soil Erosion, Enhances Fertility, and Suppresses Weeds?
- Soil Erosion Prevention: Cover crops reduce the impact of heavy rainfall and wind, preventing topsoil loss.
- Soil Fertility Enhancement: Many cover crops, especially legumes, fix nitrogen, naturally fertilizing the soil.
- Weed Suppression: Dense cover crop growth outcompetes weeds, reducing herbicide need.
Examples
- Clover adds nitrogen and improves soil structure.
- Rye suppresses weeds and prevents erosion.
- Alfalfa improves soil aeration and organic matter content.
3. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Reducing Reliance on Chemical Pesticides
IPM is a sustainable farming technique that minimizes pesticide use by integrating biological, cultural, and mechanical pest control methods. This approach protects beneficial organisms while maintaining pest populations at manageable levels.
Using Biological Controls, Natural Predators, and Trap Crops
- Biological Controls: Encouraging natural predators like ladybugs and lacewings to control aphids.
- Trap Crops: Planting crops like mustard to attract pests away from main crops.
- Cultural Practices: Adjusting planting times and using resistant crop varieties to reduce infestations.
4. Agroforestry and Silvopasture
Integrating Trees with Crops and Livestock Farming
To create a more sustainable ecosystem, agroforestry combines trees and shrubs with crops or livestock systems. Farmers in Australia often use fast growing Australian native trees in these systems, as they establish quickly, improve biodiversity and provide shade for livestock. Silvopasture is a subset where trees and pastureland are integrated to support livestock while improving land resilience.
Benefits
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb CO₂, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Soil Stability: Tree roots prevent soil erosion and improve moisture retention.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Supports beneficial insects, birds, and wildlife.
5. Conservation Tillage (No-Till or Reduced Tillage)
Definition and Impact on Soil Health
Conservation tillage minimizes soil disturbance, preserving soil structure and microbial life. No-till farming, where seeds are directly planted into undisturbed soil, significantly reduces erosion and improves moisture retention.
Equipment and Techniques Used in Conservation Tillage
- No-Till Drills: Specialized seeders place seeds without plowing.
- Strip Tillage: Tilling only narrow strips to reduce soil disturbance.
6. Water Management and Precision Irrigation
Challenges in Agricultural Water Usage
Agriculture accounts for 70% of global freshwater withdrawals, leading to severe water shortages in many regions. Sustainable irrigation methods help reduce waste while maintaining crop productivity.
Efficient Irrigation Techniques
- Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collects and stores rainwater for irrigation use.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Monitor moisture levels to optimize irrigation schedules.
Benefits
Efficient water management conserves water, improves yields, and reduces energy costs associated with pumping excess water.
7. Organic and Regenerative Farming
What Makes Organic Farming Sustainable?
Organic farming eliminates synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, relying on natural soil amendments, compost, and crop diversity to maintain fertility. It is one of the most well-known among 7 sustainable agriculture practices that support biodiversity and human health.
How Regenerative Agriculture Improves Soil Biodiversity and Carbon Storage
Regenerative farming goes beyond organic principles. It aims to restore soil health through minimal tillage, compost application, and rotational grazing.
Key Practices
- Compost Application: Enhances soil microbial activity and fertility.
- Crop-Livestock Integration: Grazing animals naturally fertilize fields.
- Soil Cover Techniques: Maintaining living roots in soil year-round to prevent degradation.
Impact on Climate and Soil Health
Studies show that regenerative farms sequester up to 3 tons of carbon per hectare annually, making them a crucial solution for mitigating climate change.
How Sustainable Agriculture Benefits Farmers and Agribusinesses
Sustainable agriculture offers farmers and agribusinesses economic, environmental, and operational advantages. By adopting sustainable farming practices, producers can reduce input costs, improve soil health, and enhance resilience against climate change.
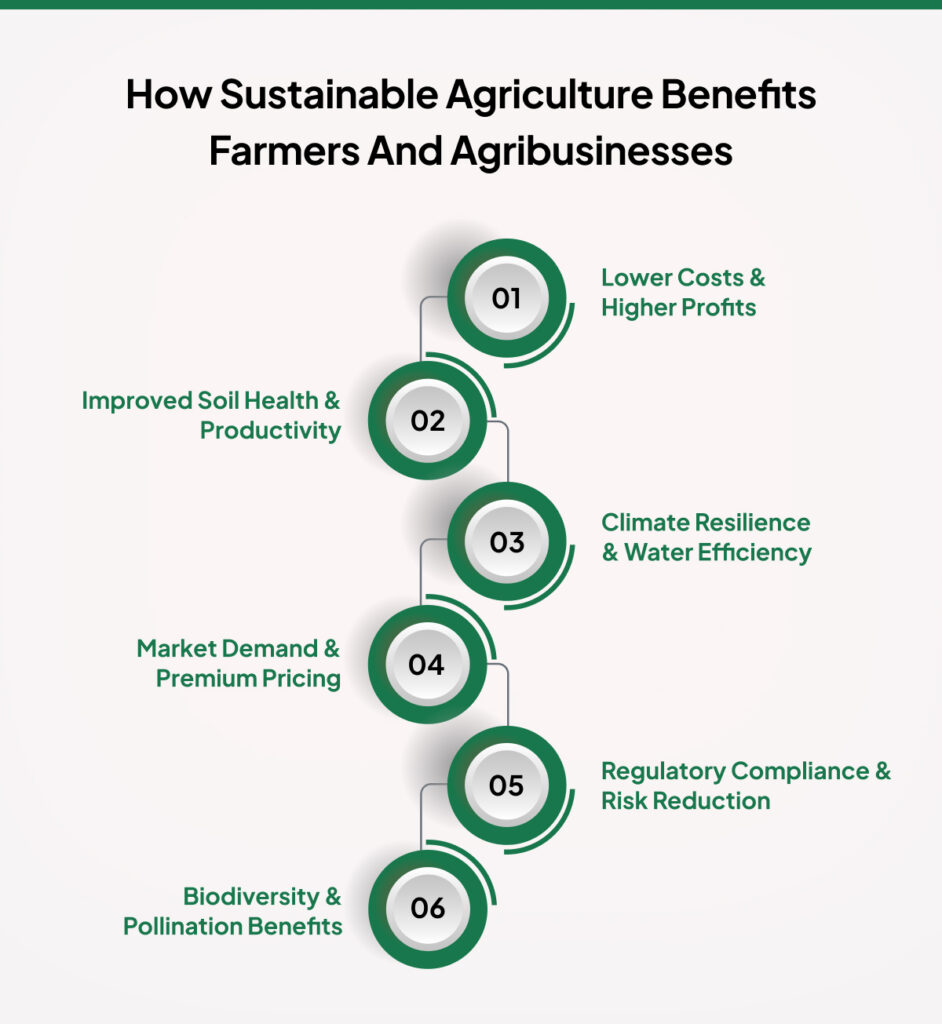
- Lower Costs & Higher Profits: Techniques like crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management (IPM) reduce reliance on expensive fertilizers and pesticides, lowering production costs.
- Improved Soil Health & Productivity: No-till farming, compost application, and regenerative methods enhance soil fertility, increasing yields over time while preventing erosion and nutrient depletion.
- Climate Resilience & Water Efficiency – Precision irrigation and agroforestry help farmers withstand extreme weather, conserve water, and maintain consistent production.
- Market Demand & Premium Pricing: Consumers prefer environmentally friendly agricultural practices, which leads to higher prices for organic and sustainably grown products.
- Regulatory Compliance & Risk Reduction: Sustainable farms meet environmental regulations, avoid fines, and qualify for government incentives supporting eco-friendly agriculture.
- Biodiversity & Pollination Benefits: Agroforestry and IPM promote natural pest control and increase pollination rates, boosting crop yields.
Challenges in Adopting Sustainable Agriculture
While sustainable agriculture offers numerous benefits, several challenges for farmers hinder its widespread adoption. Farmers and agribusinesses must navigate financial, educational, and cultural barriers to effectively implement 7 sustainable agriculture practices.
1. High Initial Investment in New Techniques
Many sustainable farming methods, such as precision irrigation, no-till equipment, and organic certification, require significant upfront costs. Although these investments yield long-term savings, small and mid-sized farmers often struggle with access to capital. Government subsidies and financial incentives can help bridge this gap, but they are not always widely available.
2. Knowledge Gap and Need for Farmer Education
Transitioning to sustainable agriculture requires specialized knowledge in soil health, crop rotation, integrated pest management (IPM), and regenerative farming techniques. Many farmers lack access to training programs, shifting from conventional to environmentally friendly agricultural practices difficult. Expanding agrarian extension services and digital learning platforms can help close this gap.
3. Resistance to Change and Reliance on Traditional Practices
Farmers who have relied on conventional farming for generations may hesitate to adopt sustainable farming techniques due to uncertainty about yields, profitability, and market acceptance. Overcoming this resistance requires strong community engagement, demonstration farms, and incentives to encourage gradual adoption.
How Folio3 AgTech Can Help in Implementing Sustainable Agriculture
Folio3 AgTech offers cutting-edge digital solutions that empower farmers and agribusinesses to adopt sustainable agricultural practices efficiently. By leveraging precision agriculture, farm automation, and AI-driven analytics, Folio3 AgTech helps optimize resource use, reduce waste, and improve farm productivity.
1. Smart Solutions for Sustainable Farming
Folio3 AgTech provides customized farm management software, enabling farmers to monitor real-time data on soil health, crop growth, and environmental conditions. These digital tools support data-driven decision-making, ensuring the effective implementation of sustainable farming methods.
2. Precision Agriculture for Water and Resource Management
Water conservation is critical in sustainable agriculture methods. Folio3 AgTech guides you to help optimize water usage, reduce waste, and enhance crop resilience to drought conditions.
3. Digital Monitoring for Crop Health & Soil Quality
Folio3 AgTech allows farmers to track crop health, detect diseases early, and assess soil fertility levels. These insights enable proactive interventions, reducing chemical inputs and promoting environmentally friendly agricultural practices.
Conclusion
Sustainable agriculture is no longer just an option—it’s a necessity for ensuring long-term food security, environmental preservation, and economic viability. By adopting sustainable farming practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, precision irrigation, and agroforestry, farmers can improve soil health, conserve water, and reduce reliance on chemical inputs.
While challenges such as high initial investment, knowledge gaps, and resistance to change exist, digital solutions like those offered by Folio3 AgTech make sustainability more accessible and profitable. Farmers and agribusinesses can use precision agriculture, AI-driven monitoring, and automated farm management tools to enhance efficiency while reducing environmental impact. Ready to make your farm more sustainable? Explore Folio3 AgTech’s solutions here and take the first step toward a greener future.
FAQs
What Is The Most Sustainable Agricultural Practice?
No single practice is the best, but crop rotation, cover cropping, precision irrigation, and agroforestry are among the most effective sustainable agriculture methods for improving soil health and resource efficiency.
What Are The 7 Principles Of Food Sustainability?
The 7 sustainable agriculture practices include resource efficiency, biodiversity, soil health, climate resilience, water conservation, social responsibility, and economic viability.
Which Is The Best Sustainable Agriculture Technique?
Precision agriculture, using IoT sensors, AI, and automated irrigation, optimizes resource use, reduces waste, and enhances yields, making it one of the most effective sustainable farming techniques.
What Do You Mean By Sustainable Agriculture Practices?
Sustainable agricultural practices are farming methods that enhance productivity while preserving natural resources, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring long-term food security.
Which Country Has The Most Sustainable Agriculture?
Denmark, the Netherlands, and Sweden lead in sustainable farming methods, implementing strict environmental policies, organic farming, and precision agriculture technologies.
How To Practice Sustainability At Home?
Grow organic vegetables, compost food waste, conserve water, and support local sustainable farms to reduce environmental impact and promote eco-friendly living.
What Are The 8 Pillars Of Sustainability?
The eight pillars of sustainable development include biodiversity, soil health, water management, energy efficiency, climate resilience, waste reduction, social equity, and economic viability.
What Are The 7 Pillars Of Food Sovereignty?
These include food for people, local control, sustainable food systems, valuing food providers, knowledge sharing, working with nature, and fair trade policies to support 7 sustainable agriculture practices.
What Are The 4 Rules Of Sustainability?
The 4 sustainability rules focus on conserving resources, reducing waste, promoting biodiversity, and ensuring economic and social responsibility for long-term environmental balance.





