Climate change isn’t a distant threat; it’s already disrupting how you farm. Unpredictable rains, harsher droughts, and new pests are making traditional practices far less reliable. To protect your food security and profits in this new reality, you need to farm smarter.
That’s where climate smart agriculture comes into play, enabling you to tackle the challenges that seem beyond control. CSA isn’t just a buzzword; it’s about farming in a way that builds climate resilience while maintaining productivity. In this guide, we’ll walk you through what climate-smart agriculture is, why it’s so important today, and how you can adopt climate‑smart practices on your farm.
By the end, you’ll see how adapting now can keep your yields steady, your soil healthy, and your agribusiness thriving even as the climate changes. It’s a conversation between us as fellow ag professionals, about practical steps to secure your farm’s future. Let’s dive in.
What is Climate‑Smart Agriculture?
Climate‑Smart Agriculture (CSA) is an integrated approach to managing farms, including crops, livestock, forests, and fisheries, that aims to simultaneously boost productivity, enhance resilience to climate stress, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In other words, climate‑smart agriculture means achieving a “triple win” in your farming operations: growing more, adapting to climate change, and cutting emissions at the same time.
The term was first defined in a 2010 report by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization. Back then, experts realized farming was caught in a bind; it is adversely impacted by climate change, yet also a contributor to climate change through emissions. CSA emerged as a solution for farmers to tackle these twin challenges while maintaining yields.
Principles & Pillars of Climate‑Smart Agriculture
What are the three pillars of climate-smart agriculture? CSA is a framework built on three core pillars that guide all climate-smart practices:
Pillar 1: Productivity
The first goal is to sustainably increase agricultural productivity and incomes. Climate-smart agriculture targets higher yields and better farm profits without degrading the land or overusing resources. It’s about producing more (or better) with less.
Pillar 2: Adaptation/Resilience
The second pillar is to adapt and build resilience to climate variability and extremes. CSA practices help your farm withstand droughts, floods, heatwaves, and shifting seasons. Resilience might mean diversifying crops, improving soil moisture retention, or safeguarding against new pests and diseases, anything that helps you bounce back from climate impacts.
Pillar 3: Mitigation
The third pillar is reducing or removing greenhouse gas emissions wherever possible (without compromising food security). It could involve sequestering carbon in soils and trees, cutting methane from livestock, or optimizing fertilizer use to lower nitrous oxide emissions. The aim is to shrink agriculture’s carbon footprint.
What makes CSA “smart” is that it tries to balance these three objectives together. In practice, that means carefully choosing strategies that create synergies between productivity, adaptation, and mitigation.
Why Climate‑Smart Agriculture Matters in the Era of Climate Change
Climate change is no longer a distant worry; it’s here and directly threatening agriculture. If you’ve noticed more erratic weather or new crop stresses, you’re not alone. Here’s the problem in numbers and facts:
Yield Declines
Research shows that under even a moderate climate change scenario, global crop yields could fall by around 8% by 2050. Heat waves, droughts, and shifting seasons are already dragging down productivity. For example, each 1°C rise in temperature can cut wheat yields by ~6% and maize yields by even more, absent adaptation. It means less grain to sell and thinner margins for you.
Water Stress
Agriculture uses about 70% of global freshwater, but changing rainfall and higher evaporation are squeezing water supplies. Many farming regions face more frequent droughts and groundwater depletion. We’ve seen the consequences in the 2015 California drought, farmers lost an estimated $1.8 billion and over 10,000 jobs due to water shortages. Around the world, wells are drying and irrigation reservoirs are under strain. Without new water-smart approaches, these trends will worsen.
Extreme Weather & Livelihoods
Climate change is driving more extreme events, such as intense downpours, floods, and storms that can wipe out harvests overnight. Smallholder farmers are hit hardest, as they often lack buffers. Unpredictable seasons also mess with planting schedules, increasing the risk of crop failure. The volatility directly threatens farmer livelihoods and rural economies.
Food Security at Risk
If we do nothing, climate change could leave millions more people hungry. By 2050, the number of people at risk of hunger due to climate change is expected to increase by 10–20% compared to a scenario with a stable climate. In parts of Africa and Asia, staple crop losses and shorter growing seasons are undermining food security. It isn’t just a humanitarian issue; it destabilizes markets and demand for agribusiness.
Policy & Donor Response
The urgency is recognized globally. Governments and donors are moving fast to promote climate-smart solutions. For instance, the U.S. launched a multi-billion-dollar Climate-Smart Commodities program (more on that later), and many countries are embedding CSA in their climate policies. The fact that policymakers are investing heavily in CSA underscores how critical it is for the future of farming.
Core Climate‑Smart Practices for Sustainable Agriculture
What do climate-smart practices look like on the ground? The following practices are tried-and-true methods many farmers are already using to get that triple win of productivity, resilience, and mitigation. As you read, think about which of these might fit your farm’s conditions and challenges.
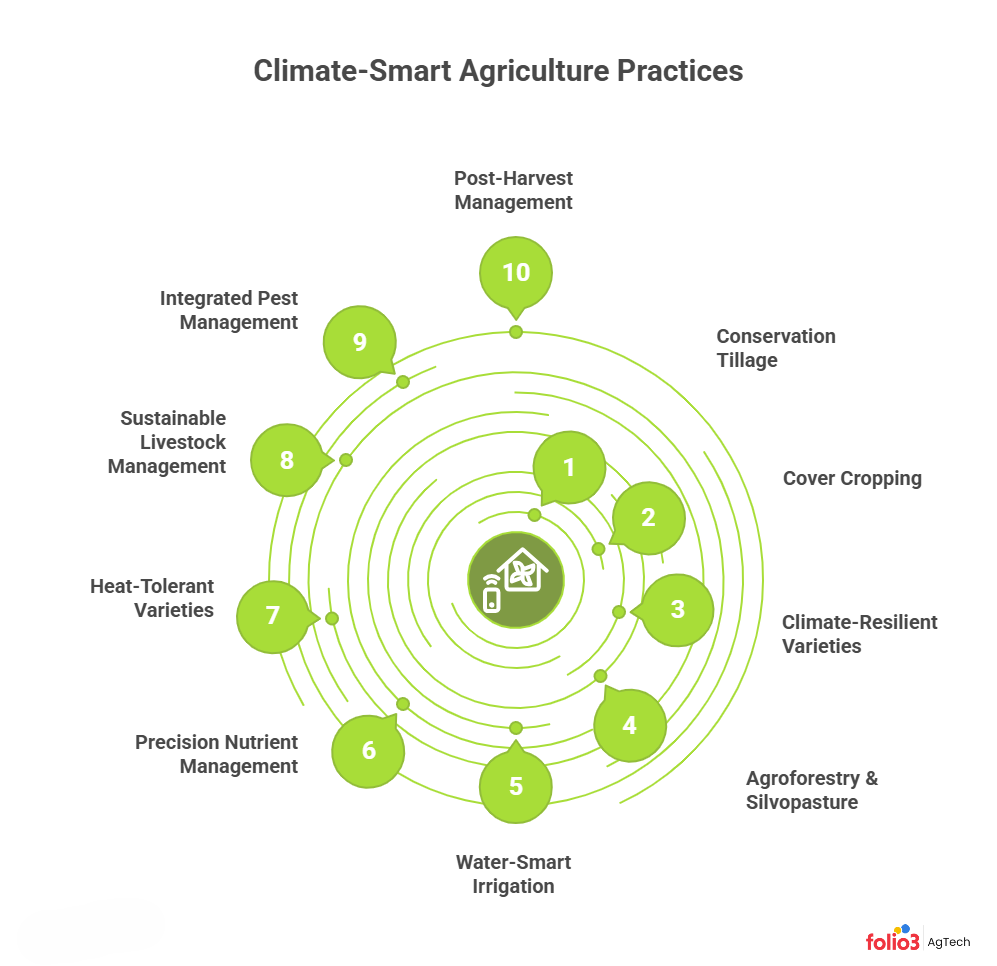
Conservation Tillage / Reduced Tillage (Soil-Friendly Farming)
Conservation tillage, like reduced or no-till farming, means disturbing the soil as little as possible. Leaving crop residues on the field protects soil from erosion, cutting losses by up to 90% compared to intensive tillage. It also helps soil retain more moisture, which can save your crops during dry spells.
From a climate perspective, conservation tillage is a win-win. Fewer tractor passes mean lower fuel costs, and carbon stays locked in the soil, improving fertility. Over time, this boosts both resilience and yields. In the U.S., around 50–70% of soybean and corn acres now use conservation tillage, a proven, climate-smart strategy worth considering for your farm.
Cover Cropping (Green Cover in Off-Season)
Cover crops like clover, rye, or vetch aren’t for sale, but they work hard for your soil. Planted after harvest, they prevent erosion, boost organic matter, suppress weeds, and improve structure. Rye scavenges leftover nitrogen; legumes like vetch fix it from the air, enriching fertility for your next crop.
However, farmers often see yield bumps from legume cover crops, for instance, increase subsequent crop yields by about 16%. They also help retain moisture during dry seasons. While timing and management matter to avoid planting delays or nutrient lock-up, with the right approach, cover crops deliver strong returns for your soil and harvest.
Climate-Resilient Varieties & Adjusted Planting Windows
Choosing climate-resilient crop varieties like drought-tolerant maize, flood-tolerant rice, or salt-tolerant barley helps you protect yields under shifting weather. These stress-tolerant options, developed by global breeders, are built for today’s challenges, but timing matters too. Climate change is altering monsoons, frost dates, and peak heat periods.
So, adjusting your planting window, like sowing early with fast-maturing, heat-tolerant wheat, can help avoid damage during sensitive stages. Farmers in South Asia and West Africa are already adapting, planting earlier or staggering sowing to sync crops with rainfall. Matching the right variety to the right time can mean the difference between a setback and a solid harvest.
Agroforestry & Silvopasture (Integrating Trees into Farms)
Agroforestry farming with trees adds shade, soil stability, and income diversity. Whether you plant timber trees with crops or graze livestock in tree-filled pastures (silvopasture), trees improve your land’s resilience. They reduce heat stress on animals and crops, helping boost milk yield or weight gain in livestock. Deep roots hold soil, reduce erosion, and enhance water retention. Shade lowers evaporation, while some setups improve water infiltration.
Plus, you gain extra income from fruits, nuts, timber, or fuelwood, especially valuable in tough crop years. Integrating trees into your farm isn’t just sustainable, it’s a smart hedge against climate shocks.
Water-Smart Irrigation & Scheduling
As water grows scarcer, smart crop irrigation systems become critical. Drip irrigation delivers water right to plant roots, cutting usage by up to 60% and boosting yields by as much as 90% in some studies. Even typical results show 20–50% water savings and stronger yields. Upgrades like pivot sprinklers or sub-irrigation help, too. But timing is key, irrigate early or late in the day, and use tools like soil moisture sensors to avoid over- or under-watering.
Many farmers now rely on tensiometers or digital probes to guide irrigation. Rainwater harvesting, farm ponds, and mulching also support water-smart management. When you manage both how and when you irrigate, you make your farm more efficient, climate-resilient, and productive with every drop.
Precision Nutrient Management (Efficient Fertilizer Use)
Using the right amount of fertilizer at the right time and place helps you save money and protect the environment. Overusing nitrogen wastes input and releases nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas nearly 300x more potent than CO₂. Underuse can reduce yields, you can control it flawlessly by leveraging a greenhouse management software.
Precision nutrient management uses soil tests, GPS maps, and variable-rate applicators to match nutrients to crop needs. Farmers often see similar or better yields with less input. According to the USDA, thoughtful nutrient planning can save about $30 per acre on over-fertilized fields, boosting profits while cutting emissions and runoff. It’s climate-smart and financially savvy, too.
Heat-Tolerant Varieties & Strengthening Seed Systems
Rising temperatures are pushing crops beyond their limits. Traditional wheat struggles above 25 °C, but new heat-tolerant lines handle 35 °C with minimal yield loss, thanks to traits like deeper roots and stay-green leaves. Drought and heat tolerance often go hand in hand. Crops like maize, millet, and sorghum are seeing significant gains.
In sub-Saharan Africa, drought-tolerant maize from the DTMA program has been game-changing. But even the best seeds don’t help if you can’t access them. Strengthening seed systems through local producers, seed banks, and awareness campaigns ensures improved varieties reach your fields on time. Plus, leveraging a seed management software can help you plant smarter and stay ahead of the heat.
Sustainable Livestock Management
Livestock farmers also have climate-smart options to reduce emissions and adapt to climate stress. Here’s how:
- Improved Feed and Diets: Better-quality feed, like legumes or high-protein grasses, improves digestion, reduces methane, and boosts animal productivity. A healthier cow emits less and gives more milk.
- Grazing Management (Rotational Grazing): Dividing pasture into paddocks prevents overgrazing and builds soil health. These managed pastures can store more carbon.
- Breeding & Genetics: Heat-tolerant breeds like Brahman help livestock cope with rising temperatures without losing productivity.
- Manure Management: Biogas digesters capture methane for energy, cutting emissions. Composting also reduces methane from manure.
- Diversification & Resilience: Mixing crops and livestock improves nutrient cycles and income stability. Shade trees in pastures reduce heat stress and support growth.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) helps you control pests without overusing chemicals. It combines tools like crop rotation, pest-resistant varieties, pheromone traps, and natural predators to keep pests below damaging levels. Instead of reacting, you prevent outbreaks through intelligent monitoring and targeted action. IPM builds resilience by supporting pollinators and beneficial insects, which thrive when chemical use is minimized.
However, climate change may bring new pests like fall armyworm, but efficient pest management helps you stay ready. Adopting IPM means scouting fields, learning predator-pest dynamics, and investing in tools like insect netting. The payoff? Lower pesticide costs, healthier ecosystems, and a stronger, climate-smart defense for your crops.
Post-Harvest Management (Reducing Losses)
Climate-smart agriculture doesn’t stop at harvest. Rising heat and erratic rains can spoil crops fast, making post-harvest management critical. Globally, about one-third of food is lost, often near the farm, due to poor storage and handling. You can cut losses with better storage (hermetic bags, silos), drying (like solar dryers), and cold chains (evaporative coolers or solar-powered cold rooms).
For perishables, losses reach 30–50%, and processing, like making dried fruit or tomato paste, extends shelf life and boosts income. With smarter harvest management, you feed more people, reduce waste, and earn more from the same harvest, even as climate risks grow.
Emerging Technologies Empowering Climate‑Smart Agriculture
Technology is a key ally in climate-smart agriculture. In recent years, a suite of next-gen tools has become available from satellites and sensors to software and AI for agriculture. Here, we’ll highlight a few categories of tech that are empowering CSA:
Precision Agriculture & Remote Sensing
Precision agriculture technology helps you manage every part of your field with pinpoint accuracy. Using GPS, drones, and satellite imagery, you can spot crop stress from drought or pests before it’s visible.
Meanwhile, tools like NDVI map flag problem zones early, so you act fast. Equipment like yield monitors, soil mappers, and weather stations feed data into variable rate tech, adjusting inputs on the go. That means fewer wasted resources and better results.
Precision ag supports climate-smart goals by cutting excess fertilizer (reducing emissions) and adapting to field conditions. With remote sensing, even insurers and governments track drought risks. Best of all, the tech is becoming more affordable and accessible for farms of all sizes.
Decision‑Support & Digital Platforms
Digital tools help you turn data into action and they have become emerging trends in agriculture. Decision-support systems (DSS) and farm management apps integrate forecasts, crop data, and market insights, becoming your 24/7 virtual advisor.
An Agriculture ERP, for instance, tracks field activities, inputs, sales, and trends, helping you plan smarter and respond to risks like pests or frost. These platforms also offer alerts (“rain expected, fertilize now”) and localized tips via SMS or apps.
Whether you run a large agribusiness or a small farm, digital tools scale to your needs. They can link you to premium markets, enable access to green finance, and provide records for sustainability claims, all while making your farm more climate-resilient and efficient.
Climate Information & Early Warning Systems
No climate-smart strategy works without timely climate information. Early warning systems (EWS) alert you to droughts, storms, frosts, or pest outbreaks, giving you time to act. Seasonal outlooks and short-term forecasts help you adjust crop choices, planting dates, or irrigation plans. For example, delayed rain predictions might prompt a switch to short-cycle crops.
On-farm warnings like frost or cyclone alerts can help you protect crops, equipment, or livestock in time. Systems like FEWS NET monitor regional risks, while local platforms provide farm-scale tips. Pest EWS can predict outbreaks like armyworms based on climate data.
You can access these services through agri-weather bulletins or apps, many of which are offered free by governments or NGOs. Some Agriculture ERPs also integrate weather APIs to deliver real-time alerts, so you’re not reacting late, but staying one step ahead.
Benefits of Climate‑Smart Agriculture
Adopting climate-smart agriculture offers a range of practical benefits for your farm and beyond. Here are some key benefits of climate-smart agriculture, framed as advantages you can expect:
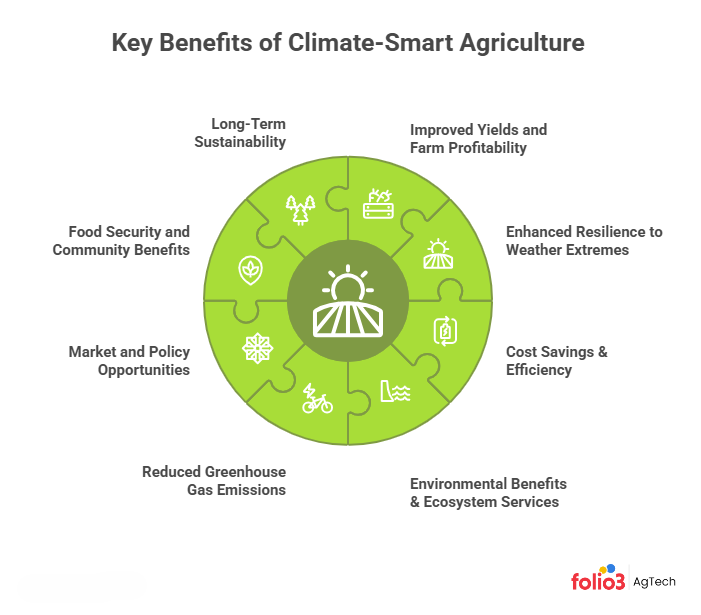
Improved Yields and Farm Profitability
CSA practices can boost productivity. For example, drought-tolerant crop varieties increase yields by 15% under stress, and techniques like precision fertilization often raise output while cutting input costs. Healthier soils and better water management translate to more stable and higher yields, which improve your bottom line.
Enhanced Resilience to Weather Extremes
Climate-smart farms are better equipped to handle droughts, floods, and storms. Practices like conservation tillage and agroforestry make soil and crops more resilient to climate shocks, reducing the risk of complete crop failure. It means less year-to-year variability and more secure livelihoods for you.
Cost Savings & Efficiency
Many CSA techniques lead to smarter resource use, saving money. Efficient irrigation (drip) can cut water use by 30–60%, saving on water bills or fuel for pumping. Precision nutrient management saves fertilizer (up to $30/acre on over-fertilized land) and fuel (fewer passes). Integrated pest management reduces spending on pesticides by leveraging natural controls.
Environmental Benefits & Ecosystem Services
Climate-smart practices improve soil health, water quality, and biodiversity on your farm. For instance, cover crops and reduced tillage build soil organic matter, while also preventing erosion and runoff (protecting nearby streams). Agroforestry and IPM provide habitat for pollinators and beneficial insects. Essentially, your farm’s ecological foundation gets stronger.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
As a bonus, CSA helps mitigate climate change. Practices sequester carbon, e.g., soils under no-till with cover crops store more carbon and cut emissions as better feed and manure management lower methane; optimized nitrogen reduces N₂O. It can open future opportunities like carbon credits or climate-friendly branding for your products.
Market and Policy Opportunities
Embracing CSA positions you to take advantage of emerging “climate-smart” market incentives. There’s growing consumer and food industry demand for sustainably produced, low-carbon products. You might access premium prices or secure contracts by demonstrating climate-smart methods. Additionally, governments are increasingly funding CSA programs, so you could benefit from grants, technical assistance, or insurance discounts by being ahead of the curve.
Food Security and Community Benefits
By maintaining productivity in the face of climate stress, CSA contributes to food security for your region. If you’re a larger producer or aggregator, your climate-smart operations mean a steadier supply for markets and potentially lower prices for consumers during extreme years. On a community level, widespread adoption of CSA can bolster rural economies and reduce disaster recovery costs.
Long-Term Sustainability
Perhaps the biggest benefit is that climate-smart agriculture is about farming with future generations in mind. It preserves the natural resource base of soil, water, and biodiversity that your children and grandchildren will rely on if they continue farming. In other words, it keeps your farm viable and sustainable for the long haul despite a changing climate.
Challenges, Trade‑Offs for Climate-Smart Agriculture
While climate-smart agriculture has many benefits, it’s not without challenges and critiques. It’s important to go in with eyes open about potential hurdles and trade-offs:
Initial Costs and Investment
Many CSA practices (like new irrigation systems, machinery for no-till, or purchasing improved seeds) require upfront investment. For small or resource-limited farmers, finding the capital or credit to implement these changes can be difficult. Without subsidies or financing support, the initial cost barrier can slow adoption.
Knowledge & Training Gaps
Adopting CSA often demands new knowledge or skills. For instance, learning to operate unfamiliar equipment, manage cover crops, or interpret climate information. Farmers may need training, extension services, or peer learning to successfully transition. In areas where agricultural advisory services are weak, this is a significant challenge.
Trade-offs Between Objectives
The “triple win” is ideal, but in reality, there are trade-offs. For instance, a legume cover crop can fix nitrogen and boost yields (productivity win), but it might also lead to higher N₂O emissions if that extra nitrogen isn’t fully utilized. Similarly, intensifying production for food security could increase emissions or water use if not balanced. Farmers have to navigate these trade-offs, sometimes prioritizing adaptation over mitigation.
Measurement and Certification Difficulties
Proving the benefits of CSA for carbon credits or market branding can be tricky. Measuring things like soil carbon increase or resilience improvements requires data and technical know-how. Many farmers lack the tools to quantify their climate impacts. It can make it hard to participate in programs that pay for ecosystem services or to counter skepticism from buyers.
Risk of Technology Dependence
There’s also the digital divide; not all farmers have access to reliable internet or tech support, so a push for digital climate-smart tools must ensure inclusivity; otherwise, it could widen gaps between large, tech-savvy farms and smallholders.
Short-Term Yield Dips or Uncertainty
Some practices, like transitioning to organic matter building or new rotations, might not pay off immediately. Farmers living on the margin might find it risky to make changes that might reduce yield in the short run, even if long-term prospects are better.
Programs & Policies Supporting CSA
The good news is that you’re not alone; a variety of programs, policies, and partnerships are emerging globally and nationally to support climate-smart agriculture. Here’s a rundown of how different actors are backing CSA, which you can tap into or at least be encouraged by:
Global Initiatives
At the international level, organizations have launched significant efforts. The Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture (GACSA), initiated in 2014, brought together 14 governments and 32 organizations at launch to enable 500 million farmers worldwide to practice CSA by 2030. While voluntary, it signaled a global commitment to transformation.
Similarly, the World Bank has mainstreamed CSA in its projects since 2015; it has increased funding for CSA eightfold to nearly $3 billion annually. Many of these investments go into developing country programs that promote sustainable land management, climate-resilient crops, and so on.
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) and other climate finance mechanisms are also pouring funds into agricultural adaptation projects, which often include training farmers in CSA practices and providing necessary tools or infrastructure.
Food Security & Development Programs
Recognizing the link between climate and hunger, programs like the FAO’s Climate-Smart Agriculture program and IFAD’s adaptation projects are active. For example, FAO’s global CSA program works on things like stress-tolerant rice in Asia and agro-pastoral field schools in Africa.
There are also research networks that develop and pilot CSA innovations on the ground. If you’re in a developing country, many of these projects operate through local extension or NGOs, which means free or subsidized access to new seeds, training, or equipment might be available through them.
National Policies – U.S. Example
In the United States, the push for CSA has taken shape in initiatives like the USDA Partnerships for Climate-Smart Commodities. This is a huge grant program, over $3.1 billion, funding 141 projects to pilot and scale climate-smart farming and forestry, especially by creating market incentives for sustainably grown commodities.
These projects involve everything from paying farmers to adopt cover crops and grazing management to developing certified climate-smart supply chains for corn, soy, beef, etc. If you’re a U.S. producer, you might engage with these through commodity groups or local cooperatives that received grants; they often provide cost-share, technical assistance, or premiums for participating farmers.
Commodity and Market Drivers
Private sector and commodity groups are increasingly on board. For instance, major food & beverage companies have sustainability sourcing goals. They may offer contracts or premiums for produce grown with verified climate-smart practices (like Rainforest Alliance certification, which covers sustainable agroforestry for coffee/tea, or programs for low-carbon rice).
Moreover, the cotton industry’s Better Cotton Initiative and some cocoa/chocolate company programs provide training and pay incentives for things like shade management or efficient fertilizer use. Even fast food chains and retailers are partnering in projects to reduce emissions in their supply chain’s agriculture segment. This trend is likely to grow, essentially rewarding CSA adoption through market access or price advantages.
NGO and Civil Society Pathways
Numerous NGOs are championing CSA, particularly for smallholders. Organizations like Concern Worldwide, Oxfam, CARE, and research bodies like ICRAF (World Agroforestry Center) run field programs introducing climate-smart techniques. They often work in partnership with local governments. Additionally, we see farmer organizations themselves leading the charge. For example, the East Africa Farmers Federation has a climate-smart agriculture agenda, disseminating drought-tolerant seeds and weather info to its members.
Climate-Smart Finance & Insurance
Innovative financing is emerging to support CSA. Some banks offer lower-interest loans for farmers adopting renewable energy or water-saving systems. Index-based climate insurance products (like weather-index insurance) are complementing CSA by providing payouts in bad climate years, which de-risks trying new practices.
Moreover, carbon credit schemes are slowly becoming accessible: e.g., smallholder agroforestry projects that aggregate farmers to sell carbon credits for the trees they plant, giving an extra income stream as a reward for CSA practices.
How a Smart Agriculture ERP Can Help You Stay Resilient Against Climate Change
As a farmer or Agribusiness owner, you must stay resilient and profitable no matter what the climate throws at you. For that purpose, one of the most powerful tools you can add to your climate-smart farming toolkit is a smart Agriculture ERP system. Here’s how an Agriculture ERP can bolster your climate resilience, with features and benefits especially relevant to climate-smart agriculture:
Centralized Data & Analytics
Our ERP brings all your farm data into one unified platform. You can record and monitor weather patterns, soil conditions, crop performance, and input use season after season. Essentially, it turns raw data into actionable climate intelligence for your farm.
Climate-Smart Planning & Resource Management
The ERP includes planning modules where you can map out crop rotations, planting schedules, and resource allocation. It can incorporate climate information, say you input a seasonal rainfall outlook, and assist in adjusting your plans. By planning with the ERP, you minimize waste and maximize your preparedness for climate variability.
Real-Time Monitoring & Alerts
An Agriculture ERP can integrate with IoT sensors and weather feeds. It means you get real-time updates on things like soil moisture, temperature, or equipment status, all visible on your dashboard. It’s like having a virtual farm assistant keeping an eye on climate risks 24/7. Timely alerts enable you to respond quickly to emerging issues, which is crucial in mitigating climate impacts. IoT powered crop health monitoring has a promising future in climate smart agriculture and leveraging it now will definitely give you an edge in the market.
Integrating Climate-Smart Practices Tracking
If you’re adopting CSA practices, the ERP can help track those activities and outcomes. You can log each practice and even monitor metrics like fuel usage, input reductions, or soil health indicators over time. If you ever want to apply for a certification, a carbon credit program, or report to a buyer, you have digital records to prove your climate-smart efforts.
Supply Chain Resilience & Market Access
On the business side, Agriculture ERP helps you streamline inventory, processing, and sales, which are crucial when climate shifts disrupt supply. You can pivot quickly, manage contracts, and maintain quality standards. With built-in traceability, you show buyers your sustainable agriculture practices, which can boost trust, unlock new markets, and even earn price premiums. It turns your climate-smart commitment into a competitive advantage.
Financial Management & Risk Mitigation
The ERP’s financial modules let you budget and monitor costs in detail. You can simulate how investing in a new irrigation management system or cover crop seed will affect your cash flow and ROI, helping you make the business case for those climate adaptations. Additionally, by keeping meticulous records of yields, losses, and expenses, you are better positioned to work with insurers or lenders.
Labor and Resource Coordination
The ERP’s task management can help coordinate your team efficiently. It ensures everyone knows what needs to be done and when, which is critical when reacting to weather events. No time is lost due to miscommunication, and you can adapt work schedules on the fly through the system.
Actionable Steps for Farmers & Agribusinesses to Put Climate-Smart Agriculture into Practice
We’ve covered a lot of ground, now let’s boil it down to a game plan. Here are six actionable steps to help smallholder farmers, farm managers, or agribusiness leaders move toward climate-smart agriculture. Think of this as a roadmap to gradually integrate the practices and strategies we’ve discussed:
1. Assess Vulnerabilities and Goals
Start by identifying your climate risks, drought, flooding, heat stress, or pests and assess how they affect your operation. Clarify goals like stabilizing yields or reducing water use. You might use a simple SWOT analysis with a climate lens. Tools from extension services can help. The goal is to map out key priorities and clear, measurable goals to guide your actions.
2. Select Appropriate Practices
Based on your assessment, choose CSA practices tailored to your farm. Drought? Go with water harvesting and resilient crops. Erosion? Try cover cropping or tillage changes. Start small, test a few practices, learn, and scale up. Consult with peers, extension officers, or Agtech experts for support.
3. Leverage Technology
Use tools like weather apps, soil sensors, or an Agriculture ERP to make informed decisions. Even basic tech, like rain gauges or WhatsApp groups, can boost your responsiveness. Assign a tech-savvy team member to lead the way if needed.
4. Access Finance & Partnerships
Explore grants, subsidies, or CSA programs for funding. Join farmer groups or work with NGOs to access tools, markets, or carbon credits. Collaboration helps reduce costs and expand opportunities.
5. Capacity Building & Knowledge Exchange
Attend training, talk to other farmers, and stay informed. Involve younger farmers; they often embrace innovation and can lead CSA adoption. Keep an eye on research, as sometimes breakthroughs can directly address your challenges.
6. Monitor, Evaluate & Adapt
Monitor the results closely by keeping records of yield data, input use, incidence of issues, etc. So, you can evaluate if the new practice is delivering the expected benefits. Use the off-season to reflect on the data and feedback, then adjust your approach for the next season.
Farming the Future, Starting Today
Agriculture is at a crossroads: we must feed a growing population, fight climate change, and adapt to its impacts, all at once. This comprehensive guide has shown that climate‑smart agriculture offers a viable path forward, helping you achieve those triple wins of productivity, resilience, and mitigation on your farm. The benefits of climate‑smart agriculture are tangible – from higher and steadier yields, to healthier soils and reduced inputs, to new market opportunities. Yes, the journey comes with challenges, but as we’ve discussed, tools, techniques, and support networks exist today to overcome them.
Now the ball is in your court. The climate is changing, but by taking action, you can change your farm for the better. So, let’s turn knowledge into action: pick a few ideas from this guide and make a plan to implement them this season or this year. Monitor your progress and don’t hesitate to seek advice or partnerships as needed. For any further queries, you can consult with our Agtech expert or book a demo to see how we can help you.
FAQs
What is the Future of Climate-Smart Agriculture?
The future of climate-smart agriculture lies in combining cutting-edge technology with sustainable practices to help you boost productivity, withstand climate impacts, and lower emissions, all at the same time. It’s a forward-looking approach that empowers you to farm smarter, not harder.
What is Another Name for Climate-Smart Agriculture?
Climate-smart agriculture is often called smart farming or smart agriculture, primarily when referring to tech-driven approaches. You might also hear the term regenerative agriculture; it’s closely related, though it focuses more on restoring natural ecosystems, while CSA takes a broader, multi-pronged approach.
What is the Climate-Smart Agriculture Fund?
The Climate-Smart Agriculture Fund refers to various funding programs that support your shift toward sustainable farming. These include USDA grants and loans in the U.S., investment programs by the Inter-American Development Bank in Latin America, and similar national or regional initiatives.
How Can Technology Help Us Adapt to Climate Change?
Technology equips you with the tools to stay ahead of climate risks, whether that’s through early warnings, smarter irrigation, or climate-resilient crop planning. Innovations like AI, satellite monitoring, and IoT devices can help you make more informed, timely decisions to protect your yields and resources.