Effective farm bookkeeping is essential for any agricultural business’s smooth operation and financial health. Whether you’re a small farm or a large-scale agricultural operation, maintaining accurate records is the foundation of long-term success.
Farm bookkeeping refers to tracking and recording all financial transactions related to a farming business. This includes everything from income generated by the sale of crops or livestock to expenses such as feed, equipment maintenance, and labor costs.
Farm bookkeeping and accounting are crucial elements of any agricultural business. Understanding bookkeeping basics is vital whether you’re a seasoned farmer or just starting your agricultural journey. Proper bookkeeping for farmers helps them understand their farm’s financial health, comply with tax regulations, and make informed decisions about the future of their business.
In this guide, we will explore why farm bookkeeping is essential, walk you through key components of farm financial management, and provide a step-by-step process to set up your bookkeeping system.
What is Farm Bookkeeping and Accounting?
Farm bookkeeping involves systematically recording and tracking all financial transactions related to a farming business. This process helps farmers maintain accurate records of income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Proper bookkeeping ensures that all economic activities are organized, enabling farmers to assess their financial health, comply with tax regulations, and make informed decisions.
On the other hand, farm accounting is a more complex practice that involves recording financial data and analyzing, interpreting, and reporting on the farm’s economic health. Unlike regular business bookkeeping, farm accounting must account for the unique aspects of agricultural operations, such as fluctuating revenue streams and diverse expenses.
Farm accounting also deals with more specialized areas such as inventory management, asset tracking (e.g., land, machinery), and debt management (e.g., loans or grants). Each category must be managed precisely to ensure accurate financial statements, tax filings, and business decisions.
Farm bookkeeping and accounting involve maintaining a clear and accurate record of every financial activity on the farm to ensure smooth operations, compliance, and long-term profitability.
Why Farm Bookkeeping is Important?
Effective farm bookkeeping and accounting are crucial for the success and sustainability of any agricultural business. Proper financial management ensures that farmers can keep track of their operations, make informed decisions, and remain compliant with regulations.
They empower farmers to track their financial health, maximize tax benefits, and make informed decisions that drive growth and profitability. Farm owners ensure they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of agricultural finance and achieve long-term success by investing time and resources into effective bookkeeping for farmers.
Let’s explore why farm bookkeeping is essential, especially in maintaining financial health, gaining tax benefits, and making data-driven decisions:
1. Financial Health
One of the most significant reasons farm bookkeeping and accounting are vital is to monitor and assess the business’s financial health. Bookkeeping for farmers involves tracking all revenues and expenses, clearly showing the farm’s profitability and financial status. With accurate financial records, farmers can:
- Track cash flow
- Manage expenses
- Evaluate profitability per field or crop
2. Tax Benefits
One of the key advantages of farm bookkeeping and accounting is the ability to optimize tax benefits. Accurate records ensure farmers comply with tax regulations and help them take advantage of tax deductions and credits they may otherwise miss. Some common tax benefits that can be maximized with proper bookkeeping for farmers include:
- Deductible expenses
- Capital gains exemptions
- Depreciation schedules
- Tax filing accuracy
3. Decision Making
Accurate farm bookkeeping and accounting are essential for effective decision-making. With comprehensive records of all financial transactions, farmers can make informed decisions that impact their operations’ growth and profitability. Whether it’s determining which crops to grow, evaluating the profitability of certain investments, or deciding whether to take on additional debt, accurate bookkeeping for farmers provides the financial insights needed for sound decisions.
Here’s how proper bookkeeping influences decision-making:
- Profitability Analysis
- Risk Management
- Long-term Planning
Key Components of Farm Bookkeeping
Farm bookkeeping covers various financial aspects that need to be managed meticulously. Let’s explore the key components:
Revenue Streams
Farming involves multiple sources of income, including sales of crops, livestock, and government subsidies or grants. Properly tracking each source ensures you understand which areas of your business are most profitable and where to focus your efforts.
Expense Management
Expenses are an important part of farm bookkeeping. These include seeds, equipment, feed, labor, utilities, and more costs. Categorizing expenses correctly helps ensure that you aren’t overlooking any fees and can identify areas where you can save money.
Asset and Liability Tracking
Tracking your farm’s assets (e.g., land, machinery) and liabilities (e.g., loans) is crucial. This will allow you to see your overall financial position and ensure you’re not over-leveraged.
Loan & Debt Management
Farmers often take out loans to finance equipment, land, or operational costs. Keeping track of the amounts owed, repayment schedules, and interest rates helps you avoid missed payments and manage your debts effectively.
Insurance & Risk Management
Farming is inherently risky, and having the right insurance coverage is essential. Tracking premiums, coverage, and claims protects your farm against unforeseen events such as natural disasters, crop failure, or livestock disease.
Inventory Management
Inventory management ensures that farmers keep track of supplies such as seeds, fertilizers, chemicals, and harvested goods. Proper farm record-keeping allows farmers to monitor stock levels, prevent over-purchasing, and avoid running out of essential items during busy seasons.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Farm Bookkeeping
An effective farm bookkeeping and accounting system ensures that a farm operates smoothly and profitably. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide to help you establish solid bookkeeping for farmers practices. This will enable you to manage your finances efficiently and gain accurate insights into the health of your agricultural business.
Step 1: Choosing the Right Bookkeeping System (Cash Basis vs. Accrual Basis)
The first step in setting up your agriculture bookkeeping system is to choose between the two primary methods of bookkeeping: cash basis and accrual basis.
- Cash Basis Accounting: This method records income and expenses when received or paid rather than when they are earned or incurred. It is simpler and typically recommended for smaller farming operations, as it provides a clear view of available cash. However, it can sometimes paint an incomplete picture of financial health, as it doesn’t account for outstanding invoices or liabilities.
- Accrual Basis Accounting: In this method, income and expenses are recorded when earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. This method offers a more accurate picture of the farm’s financial health, especially for larger operations with significant accounts payable and receivable. It is generally preferred by farms with complex transactions, such as loans, leases, or inventory management. Farms can also use an accounting AI tool to automate data recording and enhance accuracy in accrual-based bookkeeping.
Step 2: Setting Up a Chart of Accounts Tailored to Farming Operations
A chart of accounts is the foundation of farm bookkeeping and accounting. It’s a categorized list of all the accounts your farm will use to track various types of revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Setting up a chart of accounts explicitly tailored to farming operations ensures that all financial transactions are organized and classified correctly.
For a farm, your chart of accounts should include categories such as:
- Revenue Accounts: This might consist of sales of crops, livestock, or equipment, as well as any government subsidies or grants.
- Expense Accounts: Common categories here include costs related to seed, feed, labor, fuel, equipment maintenance, and utilities.
- Asset Accounts: These include land, equipment, buildings, and livestock.
- Liabilities and Loans: This category tracks loans, debts, and other financial obligations.
Step 3: Implementing Consistent Record-Keeping Practices
Consistency is key when it comes to bookkeeping for farmers. To keep your farm’s financial data accurate and up-to-date, it’s crucial to implement regular and consistent record-keeping practices. This involves:
- Tracking all transactions: Every financial transaction should be recorded in real-time, whether it’s income from crop sales or expenses like equipment repair.
- Maintaining receipts and invoices: Organize all receipts, invoices, and other supporting documents. This is essential for accurate bookkeeping, tax reporting, and audit purposes. Consider using a reliable PDF compressor to efficiently store and manage all your receipts, invoices, and supporting documents. Automate document processing to efficiently sort, categorize, and store financial documents, making retrieval faster and ensuring greater accuracy in reporting.
- Using farm-specific tools: Farm accounting software designed for agriculture bookkeeping can automate many aspects of record keeping, reducing the chances of errors and improving efficiency.
Step 4: Regularly Reconciling Accounts to Ensure Accuracy
Account reconciliation is a fundamental part of farm bookkeeping and accounting. It involves comparing financial records to external documents such as bank statements, credit card statements, or loan statements to ensure that the books are accurate and current.
- Bank Reconciliation: Regularly compare your farm’s bank account statements with your financial records to ensure that all transactions, such as deposits and withdrawals, match.
- Loan and Credit Account Reconciliation: Check that all outstanding loans or credit balances are accurately recorded in your accounts.
- Expense Matching: Ensure all business expenses are accounted for and all payments have been included and correctly recorded.
Step 5: Generating Essential Financial Reports
Once your farm bookkeeping and accounting system is in place and running smoothly, the next step is to generate and review essential financial reports. These reports provide crucial insights into your farm’s financial health and can help you make informed decisions. The three most important economic reports for farmers are:
- Profit & Loss Statements: This report summarizes your farm’s revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period, helping you understand whether your farm is making a profit or running at a loss. It also highlights areas where costs can be reduced or revenues increased. For students studying farm management or agribusiness, learning how to analyze these reports is essential and some may choose to get help with statistics homework on time to better understand the financial data and calculations involved.
- Cash Flow Statements: This document tracks the cash movement in and out of the farm’s accounts. It helps ensure the farm has enough liquidity to meet operational needs, such as paying bills and managing payroll.
- Balance Sheets: A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your farm’s financial position at a given time. It lists assets (land, livestock, and equipment), liabilities (like loans and debts), and equity. This report is vital for assessing your farm’s solvency and financial stability.
Common Mistakes in Farm Bookkeeping
Effective farm bookkeeping and accounting are crucial to running a successful farming operation. However, many farmers make common mistakes, leading to inaccurate financial records, tax issues, and poor decision-making. Identifying and avoiding these mistakes is essential to maintaining financial health and ensuring that your agriculture bookkeeping efforts yield the best results.
Below are some of the most common mistakes in bookkeeping for farmers, along with tips on avoiding them.
1. Misclassifying Expenses
One of the most common mistakes in farm bookkeeping and accounting is misclassifying expenses. Farmers often have many expenses, from seed purchases to equipment repairs and fuel costs. However, if these expenses aren’t appropriately categorized, they can lead to confusion when generating financial reports like Profit and loss Statements or Balance Sheets. Misclassifying expenses can also have tax implications, as it may lead to incorrect deductions or overstatements of profits.
2. Ignoring Small Expenses
Another common mistake in agriculture bookkeeping is paying attention to small expenses. While small purchases may seem insignificant initially, they can add up quickly over time and considerably impact your farm’s financial performance. Overlooking minor expenses can distort the accuracy of your Profit & Loss Statements and lead to incorrect projections of cash flow and profitability.
3. Lack of Documentation
The most critical mistake farmers make in bookkeeping for farmers is failing to keep proper documentation. With receipts, invoices, or other supporting records, it’s easier to verify the accuracy of financial transactions, which can lead to problems during tax season or audits. The IRS, in particular, requires that all business expenses be documented to support tax deductions. Lack of documentation can also result in fines or penalties if your farm is ever audited.
Farm Bookkeeping Best Practices
Maintaining proper farm bookkeeping and accounting practices is essential for any farmer looking to manage their finances effectively, stay tax-compliant, and make sound financial decisions. By following these best practices, farmers can ensure that their agriculture bookkeeping is accurate, efficient, and aligned with industry standards.
Below, we outline some of the most important bookkeeping best practices for farmers to help you manage your farm’s financial health.
1. Regular Updates
One of the most crucial best practices for farm bookkeeping is ensuring regular updates of your financial records. Procrastinating and allowing transactions to pile up can lead to missed details, mistakes, and inaccurate financial reports, which can have significant consequences. Regularly updating your records will allow you to track cash flow, expenses, and profits more effectively and ensure your financial data is always accurate.
How to Implement Regular Updates?
- Daily or Weekly Entries: Make it a habit to enter all financial transactions into your agriculture bookkeeping system daily or weekly. This includes recording all income, expenses, and asset purchases.
- Set Reminders: Use reminders or digital tools to help you stay on top of this task. Farm accounting solutions and apps can automatically sync bank transactions, saving you time on manual entries.
- Revisit Budget & Forecasts: Regularly update your budget and financial forecasts to reflect changes in revenue or expenses. This will help you maintain economic control over your farm.
2. Reconciliation
Reconciliation is a critical step in farm bookkeeping and accounting that ensures your financial records match your actual bank accounts and credit card statements. Regular reconciliation helps identify errors, discrepancies, or fraudulent activities early, preventing them from becoming bigger issues. It’s also essential to maintain accurate Profit & Loss Statements, Cash Flow Statements, and Balance Sheets, which depict your farm’s financial health.
How to Reconcile Your Accounts?
- Compare Bank Statements with Records: At least once a month, compare your bookkeeping for farmers’ records with your bank statements to ensure they match. This includes accurately recording all income, expenses, and transfers.
- Reconcile All Accounts: Don’t just focus on your checking account—ensure that credit cards, loans, and other financial accounts are reconciled as well.
- Use Farm Management Software: Many agriculture bookkeeping tools offer automatic reconciliation features, making it easier to match transactions with bank records.
3. Audit Preparation
While audits may only happen in some years, preparing for one in advance is still essential. Proper farm bookkeeping can make an audit much less stressful, as well-organized records and transparent financial practices will allow you to respond to any questions or requests from auditors quickly. Preparing for an audit means keeping thorough and organized financial records and following best practices year-round.
How to Prepare for an Audit?
- Maintain Thorough Documentation: Keep receipts, invoices, and other supporting documents for all farm transactions. These are essential during an audit, especially for justifying tax deductions.
- Keep Accurate Financial Reports: Regularly generate Profit & Loss Statements, Balance Sheets, and Cash Flow Statements. This provides a snapshot of your financial health and can be used as evidence in case of an audit.
- Follow Accounting Standards: Stay current on the accounting principles and tax laws relevant to your farm. This includes choosing the correct accounting method (cash vs. accrual) and accurately reporting revenue and expenses.
Advanced Farm Bookkeeping Techniques
As your farm business grows and becomes more complex, it’s important to move beyond basic farm bookkeeping and accounting to more advanced techniques. These techniques help you manage larger operations, optimize profitability, and ensure that your farm remains financially sustainable.
Below, we explore three advanced agriculture bookkeeping techniques that can elevate your bookkeeping for farmers’ practices: budgeting and forecasting, cost analysis, and financial reporting.
1. Budgeting and Forecasting
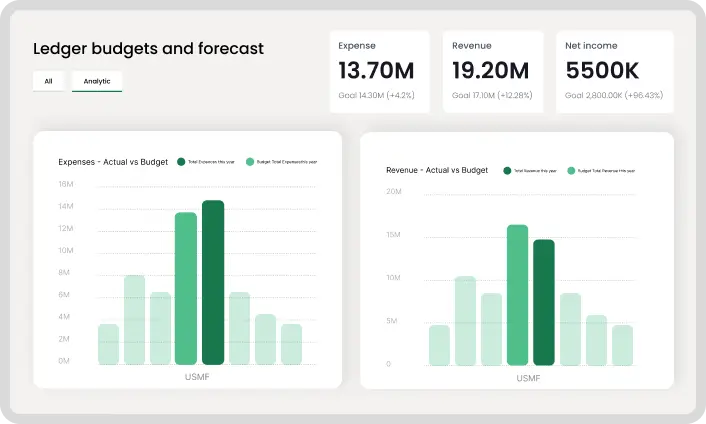
Effective budgeting and forecasting are critical components of advanced farm bookkeeping. They provide farmers with a financial roadmap, helping them plan for the future and make informed decisions. By forecasting future revenues, expenses, and profits, you can identify potential challenges and opportunities ahead of time. A solid budget helps you allocate resources efficiently and avoid cash flow problems.
2. Cost Analysis
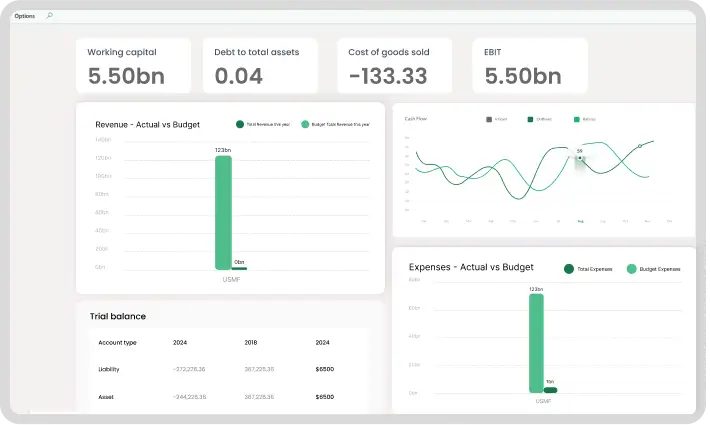
Cost analysis is a critical agriculture bookkeeping technique that involves identifying, assessing, and managing the costs associated with running your farm. By conducting regular cost analysis, you can pinpoint inefficiencies, reduce waste, and optimize resource allocation. This allows you to maximize your farm’s profitability and minimize unnecessary expenses.
3. Financial Reporting
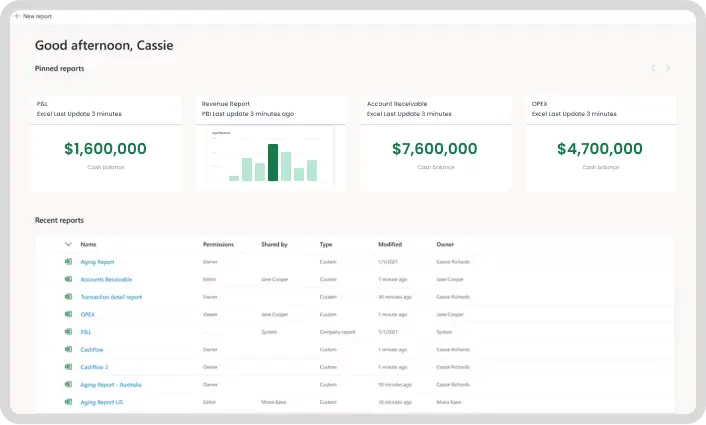
Financial reporting is an essential part of advanced farm bookkeeping. Regularly generating financial reports—such as Profit & Loss Statements, Cash Flow Statements, and Balance Sheets allows you to track the overall health of your farm and make data-driven decisions. These reports give you insight into your farm’s profitability, liquidity, and financial stability, providing the information needed to take the next step in your farm’s growth.
Conclusion
Effective farm bookkeeping is essential for maintaining any agricultural business’s financial health and sustainability. By tracking income, managing expenses, and making data-driven decisions, farmers can stay compliant with tax regulations and position their businesses for long-term success.
For farmers looking to streamline their bookkeeping and financial management processes, Folio3 AgTech offers advanced solutions tailored to the agriculture sector.
FAQs
What Are Farm Bookkeeping and Accounting, and Why Are They Important?
Farm bookkeeping and accounting involve recording, tracking, and analyzing financial transactions specific to agricultural businesses. This ensures proper financial management, helps in budgeting, and simplifies tax compliance for farmers.
How is Bookkeeping For Farmers Different From Other Industries?
Bookkeeping for farmers accounts for unique factors like crop cycles, equipment depreciation, and government subsidies. It also includes tracking expenses like livestock feed, fertilizer, and seasonal labor costs, unique to agriculture.
What Tools Can Help Streamline Agriculture Bookkeeping?
Farmers can use specialized software like QuickBooks, Xero, or Ag-specific platforms like FarmBooks to automate transaction recording, expense tracking, and financial reporting, saving time and reducing errors while benefiting from a quickbooks discount.
How Can Accurate Bookkeeping Benefit a Farming Business?
Accurate bookkeeping provides clear insights into profitability, supports better decision-making, helps secure loans, and ensures compliance with tax regulations, which is crucial for sustainable growth in agriculture.