Food manufacturers across the world always try to keep a close eye on the quality of the products being processed. Any negligence or compromises made to the quality of food products can result in serious consequences for both the consumers and the manufacturers involved.
According to statistics shared by WHO, one in 10 people in the world falls ill after eating contaminated food, and around 420,00 people die every year due to foodborne illnesses. To keep these numbers as low as possible, food companies play a significant role in maintaining food quality throughout the supply chain.
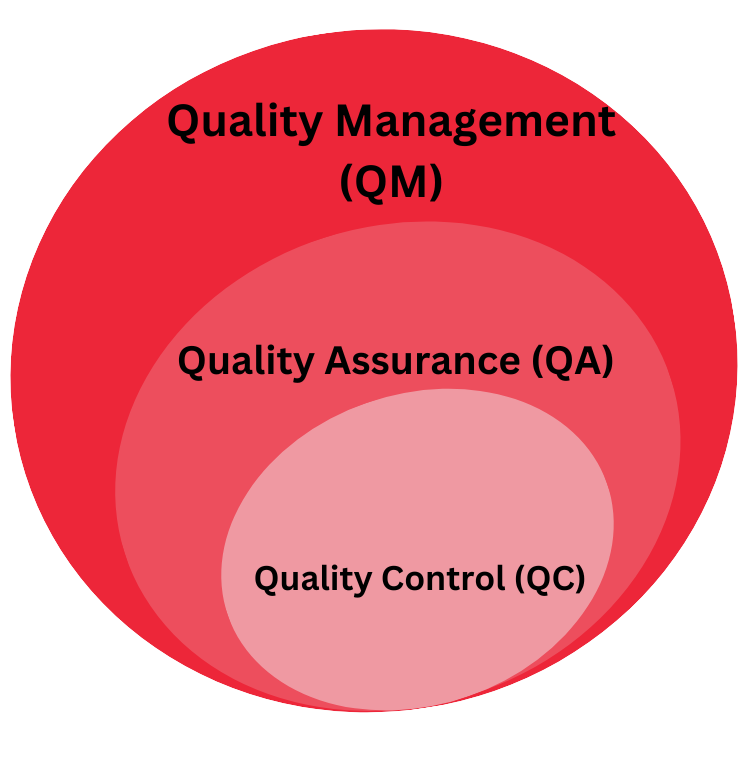
Food quality control (QC) and food quality assurance (QA) are two critical aspects of the food industry that help food businesses ensure the safety and quality of products. They are responsible for implementing and maintaining strict standards and protocols to ensure the food produced is safe, nutritious, and free from contaminants or harmful substances.
In this blog, we will explore the significance of food quality control and assurance. By the end, you will have a thorough understanding of the differences between quality control and quality assurance, the best practices for implementing QC, and how food safety software can help in the process.
Understanding Food Quality Control and Its Significance
The term “quality control” refers to the set of procedures that a business follows to ensure that the quality of the product manufactured is maintained or improved. Food quality control involves testing and inspecting products at different manufacturing stages to meet food safety standards and customer requirements.
It includes monitoring ingredients, storage conditions, processing methods, and packaging to prevent any potential contamination.
Importance of Quality Control
There are many reasons why food manufacturing businesses should never underestimate the importance of quality control in food industry. Following are some of those factors mentioned:
1. Food Safety:
Quality control in food industry helps identify food contamination, which can be of three types: physical, biological, and chemical. By applying the right food quality control procedures, businesses can identify defects and take action on time. If these steps are not taken, foodborne diseases might develop, harming consumers and damaging the company’s reputation.
2. Compliance with Regulations:
The food industry is heavily regulated by different government organizations operating in every country. For example, in the United States, the FDA sets quality standards for food businesses. Compliance with standards is very important; otherwise, it could lead to monetary fines and penalties. Hence, food quality control measures involve the business complying with the regulations and standards set by food regulatory bodies.
3. Consumer Trust:
By maintaining food quality control measures, the products produced are consistent, and consumers receive high-quality products every time. This builds up brand loyalty in the consumer’s mind, and he trusts that he will get it of the same quality whenever he buys a food product from that brand.
Hence, delivering high-quality products consistently can help the brand retain its customers and build a loyal customer base. This could be a great competitive edge for any food company in today’s highly competitive market.
4. Reduced Production Costs:
Food quality control procedures can help identify defects early in the production process. This can reduce wastage and prevent low-quality products from entering the market. It can also help identify areas for process improvement, which can lead to production efficiency. Thus, implementing measures for quality control in food industry can ultimately lead to cost savings for the business.
Examples of Quality Control in the Food Industry
There are various QC measures that companies operating in the food industry can take in order to maintain the quality standards of their products. Here are examples of some of the procedures:
Ingredient Specifications
If a company wants the final product it supplies in the market to meet quality standards, the first step is to get the right raw materials. Each ingredient used in the product should have proper specifications, including its source, purity, and any other requirements.
For example, a company that produces tomato sauce must specify the level of ripeness, acidity, and sugar content of tomatoes.
Approved Supplier List
Apart from ingredient specifications, the food business must have an approved list of suppliers from which it procures raw materials for production. The quality assurance and procurement team must work together to review and update the supplier list on a regular basis. The approved suppliers must meet specific quality standards and have proper certifications and documentation to ensure the safety of their products.
Product Formulation/Recipe
Once the right set of raw materials is on the table, the production team should formulate a product recipe. The primary purpose of having a recipe is to make sure that the product manufactured every time is of the same quality. The team needs to follow proper instructions, which include the recommended weights, batch size, and process time. The production team must document everything they do.
Manufacturing Procedures
Manufacturing procedures are documents with all the steps involved in the production process. Every bit of detail related to the production of food is documented. For example, a dairy plant has detailed procedures for pasteurization, homogenization, and milk packaging. These procedures include time and temperature controls to ensure the milk is free from harmful bacteria.
The documents should be easy to read, and every step must have a specific purpose. This is essential as it provides guidelines and instructions on consistently producing high-quality products in large quantities.
In-Process Records
In-process records, again, are documents that contain all the processing details of a product during its manufacturing. Recording details like batch size, process time, temperatures, product weights, etc., can help identify any issues that may arise later on. Moreover, having such details can help maintain the consistency of manufacturing products.
Labeling & Packaging
One of the most important components of quality control in food industry is accurate labeling and packaging. This is important for maintaining product quality and communicating the right information to the consumers about the ingredients, nutrition, and usage information.
For example, a juice company ensures each bottle has an accurate label with information about ingredients, allergens (if any), nutritional facts, and expiration date.
Technology Integration
Implementing advanced technological tools can enhance the food quality control process. IoT devices like sensors and scanners can monitor the production process in real-time and detect any issues or deviations from quality standards. Record-keeping software can also be connected to the devices to digitize data collection and perform analysis.
For example, Folio3 FoodTech food safety software can help companies maintain QC by digitizing food safety with automated HACCP plans and templates that can save up to 30% more time on food safety tasks.
Developing and Implementing Effective Quality Control Program
So far, we have seen the importance of quality control in the food business and have gone through a few examples of quality control measures. To consolidate all these details, we will now have a look at the 5-step model of building a food quality control program that any business can implement:
Step 01: Create a Quality Control Plan
The first step is to create a QC plan. This plan should entail the specific quality standards that the company wants to meet, how it will do so, what tools and measures will be used, and who will be responsible for implementing them. It must also include details on materials and equipment used and their SOPs.
Step 02: Establish a System for Inspection and Testing
The next step is to build a system for regular inspection. Everything in the production facility should be constantly monitored and tested, be it the raw materials, the equipment, or the product itself. Documentation must be done in order to review if everything is up to the QC standards.
For example, if a company uses raw milk, it must be tested daily for bacterial contamination and the results should be documented to ensure it meets safety standards before processing.
Step 03: Conduct Regular Audits and Reviews
While daily checks are necessary, businesses should schedule periodic audits and reviews to verify compliance with QC procedures. The audit team can use checklists to review documentation, inspect processes, and interview employees. Any non-conformities or deviations from standard procedures must be reported, and corrective action must be taken.
For example, if an audit reveals improper cleaning practices, the business should implement revised protocols and training. This will also help the company prepare better for external audits.
Step 04: Establish a Customer Complaint Response System
The quality control program must also develop a system for handling customer complaints. Without this, quality control in food industry cannot be effectively performed. Companies can set up a hotline or circulate an online form that consumers can fill out to report their complaints. A process must be made to ensure these complaints are resolved on time and required action is taken promptly.
For example, if a consumer reports finding foreign objects in a packaged food item, the company should investigate and manage food recall for any affected products.
Step 05: Track and Analyze Product Quality Data
Last but not least, tracking product quality data is important to identify trends and make necessary changes in the production process. Companies can use data analytics tools to analyze the collected data, identify potential issues, and improve the overall QC program.
To perform this step in the best possible way, companies can use food safety software systems that help them avoid using paper-based forms and manual data entry. The software allows tasks to be monitored 24/7, and all compliance documents/checklists can be stored or updated digitally.
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance: Major Differences and Challenges
Businesses often use quality control and quality assurance interchangeably, but it is important to understand the difference between them. Both quality control and quality assurance are part of quality management processes that businesses adopt in order to make sure the products they supply in the market are free of any contamination or hazards.
QC, however, is a subset of quality assurance. It is often regarded as a reactive process that identifies and corrects defects or deviations from standards during production. On the other hand, quality assurance is a proactive process that focuses on preventing issues before they occur.
Food quality assurance is a set of activities designed to ensure that a company’s processes are adequate for producing quality products. The first step in achieving QA in food processing is to have an effective Hazard and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan.
This plan helps establish critical points to monitor the flow of food, identify potential hazards in the production process, and develop preventive measures to eliminate them. It is also important to have an Equipment Maintenance Plan that ensures all equipment is functioning correctly and safe for use.
Challenges of Maintaining High Standards of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
While we have discussed quality control and quality assurance in detail, managing these two processes is not quite easy. Companies face many challenges while maintaining food quality control and assurance. Here are some of the challenges discussed:
- Inconsistent Regulations: The food industry is highly regulated. However, these regulations differ from country to country. In such circumstances, a business operating globally might find it difficult to maintain QA and QC as per each country’s standards.
- Lack of Resources: Maintaining food quality assurance is a huge task that requires separate teams with specific expertise. However, not all businesses can afford to have such resources. Smaller companies may find it difficult to maintain quality standards because they often cannot afford to allocate resources for this.
- Cost Constraints: To have a proper quality control management system, companies need software solutions to maintain all the data and documentation in one place. However, implementing such systems can be expensive for some businesses, making it challenging to maintain high standards.
- Human Error: Despite having strict quality control measures and protocols in place, human error is inevitable. With the large amount of data that needs to be collected and monitored, it is common for employees to mistakenly enter incorrect information or miss critical points during inspections.
How Food Safety and Compliance Software Helps in Maintaining Quality Control
Food safety and compliance software, such as the one offered by Folio3 FoodTech, can help companies digitize their record-keeping process. This is the biggest pain point of companies operating in the food industry. Most inspection and QC teams use paper-based forms to review the production processes and perform audits.
To digitize this process, Folio3 FoodTech’s food safety and compliance software comes with features such as digital checklists, automated data collection and analysis, an online complaint management system, and HACCP plan templates. This helps companies maintain all the records in one place and ensures accurate data collection, which is essential for effective QC. Also, when external audit teams visit the food processing facility, the business can have all the necessary documents and checklists readily available for review, saving time and effort.
Conclusion
All in all, to achieve quality management success, food companies need to make sure that their production process is up to quality standards and that food safety and quality are not compromised at any level. High-quality raw materials must be used, everything happening during production must be documented, and regular audits and reviews must be conducted to maintain quality standards.
Additionally, investing in food safety and compliance software can go a long way in ensuring an efficient and effective quality control process, which makes it easier for businesses to comply with regulations and ensure customer satisfaction. By following the steps discussed in this article, companies can establish an effective quality management system and mitigate potential risks associated with production.
FAQs
What is the Food Quality Control Point?
The food quality control point is a particular stage of the food production process where measures are taken to make sure the quality and safety of the product are maintained. Taking the measures at critical control points helps prevent hazards.
What are the Principles of Food Quality?
Major principles of food quality include food safety, nutritional quality, sensory characteristics (taste, appearance, texture), and shelf life. A balance between these principles is essential to ensure the overall quality of the product.
What is TQM in Food?
TQM is Total Quality Management in food processing, a management approach focusing on continuous improvement of processes and outputs. TQM principles include customer focus, process optimization, and employee involvement to ensure quality standards are met throughout production.
What is ISO for Food Quality?
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is a set of international standards that provide guidelines for establishing and maintaining a quality management system. ISO 22000 specifically focuses on food safety management systems, ensuring food companies comply with international standards for quality assurance and control.