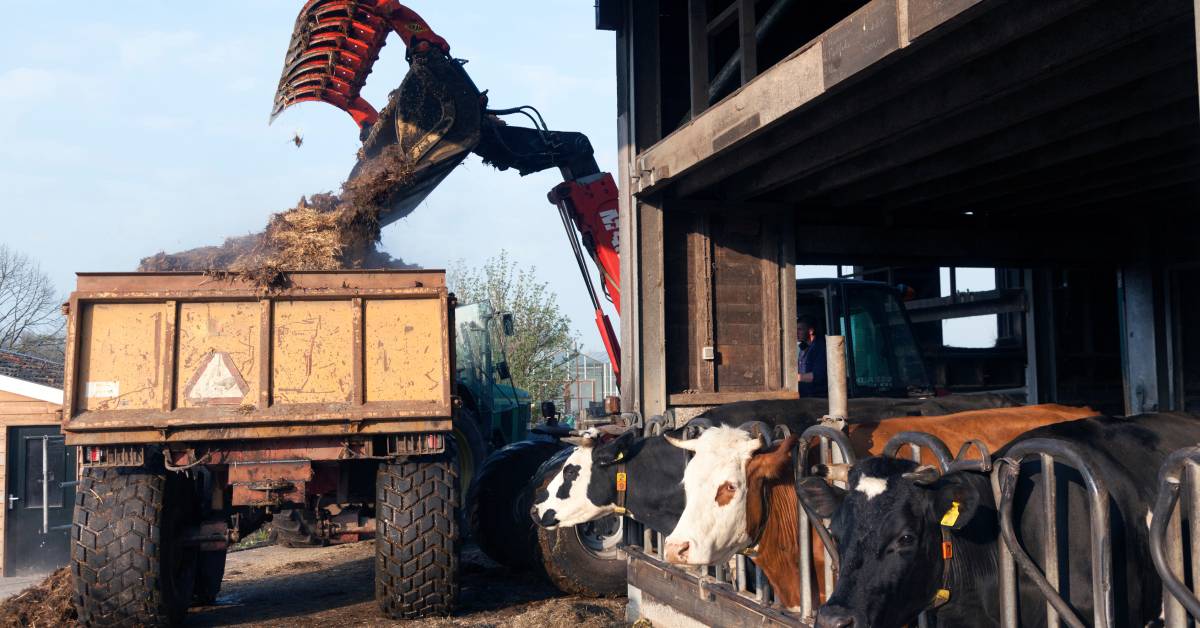
Beef feedlots generate around 1,800 kg of dry manure per animal annually, creating both environmental challenges and resource opportunities. During a typical 150-day finishing period, each animal produces about 900 kg of collectible dry manure, according to research. Managing this large volume of waste is crucial to preventing water contamination, reducing operational costs, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
With increasing scrutiny from regulatory bodies and local communities, poor manure management can lead to fines, reputational damage, and animal health issues. However, when handled properly, manure transforms from a liability into an asset, enhancing soil fertility, supporting sustainable crop production, and improving overall farm profitability.
This shift in perception reflects a growing trend among forward-thinking feedlot operators who now view manure as a valuable input rather than a disposal problem. Effective manure management not only ensures environmental stewardship but also unlocks long-term economic benefits for livestock operations.
This blog explores top manure management strategies for beef feedlots, offering practical solutions to turn waste into value while promoting environmental stewardship. By shifting the perspective from waste disposal to resource optimization, feedlot operators can meet regulatory standards, strengthen community trust, and build more resilient operations.
Understanding Manure Management in Beef Feedlots
When it comes to beef feedlots, understanding the fundamentals of managing manure provides the foundation for implementing effective strategies that serve both operational and environmental objectives. It is a strategic move that can have a direct impact on your bottom line.
How Manure Management Systems Work in Beef Feedlots?
Manure management works best when approached as a complete system, covering every stage from collection and storage to treatment and application. There’s no universal formula; each feedlot needs a tailored plan based on factors like climate impact, soil type, regulatory requirements, and local demand for manure-based products.
But successful feedlots don’t view manure management as a burden. Instead, they treat it as a core business function, integrating it with animal nutrition planning, crop production goals, and environmental compliance efforts. The result? A system that’s cleaner, more efficient, and more profitable.
Why Facility Layout Matters?
The physical layout of your feedlot plays a critical role in how efficiently manure can be collected and managed. A well-designed layout encourages proper drainage, minimizes runoff, and allows for gravity-assisted manure flow to centralized collection points.
This not only reduces the need for heavy labor and machinery but also limits the risk of environmental contamination. Sloped pen surfaces, correctly positioned alleyways, and accessible storage structures all contribute to a smoother, more cost-effective manure management process.
Key Components of Manure Management Systems
Manure management in beef feedlots involves more than just waste removal—it’s about optimizing every stage of the process. From the collection of manure to its processing and utilization, each step plays a crucial role in driving both feedlot efficiency and sustainability.
Operators must consider local conditions, regulatory requirements, and opportunities for nutrient reuse to build a system that adds value rather than imposes a burden. Below are the key components of manure management systems:
1. Manure Collection
Manure is removed from pens using scrapers, loaders, or flushing systems. Frequency varies based on weather, pen conditions, and stocking density, typically ranging from weekly to monthly.
2. Storage Solutions
Storage systems such as lagoons, solid storage structures, or composting areas must be designed to handle varying volumes while preventing runoff or leaching.
3. Treatment Options
Treatment methods include aging, composting, or anaerobic digestion. These processes reduce pathogens, odors, or concentrate nutrients depending on operational goals and regulatory standards.
4. Utilization and Application
Processed manure is applied to cropland or sold to external markets. Nutrient application must align with crop needs to avoid overapplication and runoff.
5. Integrated Planning
The most efficient feedlots embed manure management into overall business strategy, coordinating across nutrition, facility design, compliance, and crop production to maximize value and minimize environmental risks.
Why Does Manure Management Matter for Feedlot Operations?
Instead of viewing manure as a waste issue, leading feedlot operators are turning it into a performance lever. Smart manure management contributes directly to cleaner pens, healthier cattle, fewer regulatory headaches, and even long-term cost savings.
By treating manure as a resource rather than just a compliance concern, operators can improve operational efficiency, reduce reliance on commercial fertilizers, and create opportunities for additional revenue streams. It’s not just about staying compliant, but it’s about building a feedlot operation that’s cleaner, leaner, and future-ready.
What Environmental and Operational Impacts Should You Consider?
Effective manure management isn’t just about waste removal. It’s about understanding the broader environmental and operational consequences of how manure is handled. Poor practices can lead to pollution, health risks, and regulatory penalties, while smart strategies help protect resources, improve herd performance, and ensure long-term viability.
1. Water Contamination and Ecosystem Risk
Manure runoff can pollute nearby water bodies, triggering algal blooms, reducing oxygen levels, and harming aquatic ecosystems. This creates legal risks, cleanup costs, and reputational damage for feedlot operators.
2. Air Quality and Odor Management
Unmanaged manure emits ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and dust, which degrade air quality and cause respiratory issues in cattle and workers. These odors can also result in complaints from nearby communities and increased regulatory oversight.
3. Animal Health and Productivity
Wet or manure-laden pens raise the risk of lameness, foot rot, and respiratory diseases. These health issues lower feed conversion efficiency and reduce overall weight gain, directly impacting profitability.
4. Regulatory and Legal Pressures
Environmental agencies are imposing stricter standards for waste management. Operations lacking robust manure systems risk non-compliance penalties, increased scrutiny, and potential shutdowns.
What Are the Most Effective Manure Management Strategies for Beef Feedlots?
Modern feedlot operators have access to proven strategies that can transform manure from a liability into a valuable resource. The key lies in selecting the right combination of approaches for your specific operation.
1. Safe and Efficient Manure Storage Practices
Proper manure storage is foundational to effective feedlot management. The selection of a storage system, such as lagoons, composting systems, or solid storage, should align with your operation’s climate, soil type, and regulatory obligations.
- Lagoon systems provide long-term, moisture-tolerant storage, making them ideal for regions with suitable soils and a safe distance from water sources. Key design features include impermeable liners, sufficient freeboard, and overflow protection to prevent contamination.
- Composting systems not only reduce volume and kill pathogens but also produce a stable, high-value end product. While requiring more oversight, specifically control over moisture, oxygen, and heat, the return on investment comes from improved nutrient retention and lower transportation costs.
- Solid storage systems enable controlled application timing and are suitable for operations emphasizing nutrient precision. These setups require protection from rain and measures to prevent runoff, but they offer great flexibility and promote nutrient conservation.
2. Manure Handling Best Practices to Keep Feedlots Clean and Compliant
Effective manure handling is crucial for maintaining feedlot hygiene, ensuring environmental compliance, and maximizing nutrient utilization. It includes all activities post-storage to preparation for field application.
- Routine scraping and removal prevent buildup, reduce disease risks, and maintain clean, dry surfaces for livestock.
- Moisture control during handling ensures manure maintains a usable consistency, whether for composting, transport, or spreading.
- Runoff and leachate prevention through buffer zones, slope management, and impermeable surfaces minimizes nutrient loss and protects nearby water bodies.
3. Manure Application Methods to Improve Soil Health and Crop Yield
Proper manure application isn’t just about getting rid of waste. It’s an opportunity to enhance soil health, boost crop yields, and reduce nutrient loss. For beef feedlot operators, adopting innovative application methods ensures that manure nutrients are utilized efficiently while maintaining operations that are both compliant and sustainable.
Here’s how you effectively apply manure:
- Match Timing with Crop Needs: Apply manure when crops can use the nutrients, typically before planting or during active growth. Avoid applying during rainy seasons or periods of frozen soil to prevent runoff and leaching.
- Use Injection Systems for Precision: Injection systems place nutrients directly into the root zone, minimizing ammonia loss and odor, reducing runoff, and enhancing nutrient uptake. While they require a higher initial investment, they offer long-term agronomic and environmental benefits that often outweigh the costs.
- Surface Application with Timely Incorporation: Surface application remains widely used due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, it must be carefully timed and quickly incorporated into the soil to minimize nutrient volatilization and runoff. The best results are achieved when the soil is not saturated and rain is not expected.
- Split Applications for Better Efficiency: Dividing manure applications into multiple smaller doses helps align nutrient availability with crop uptake, reducing the risk of over-application and nutrient loss. This approach supports more consistent crop growth and improved yields throughout the growing season.
- Use Precision Application Technology: GPS-guided systems and variable rate applicators optimize nutrient application by adjusting rates based on soil test data and crop requirements. This enhances nutrient use efficiency, minimizes waste, and generates digital records that support regulatory compliance, traceability, and data-driven decision-making.
4. Composting Techniques for Value-Added Manure Products
Composting transforms raw manure into a stable, nutrient-rich product with substantial market value. When appropriately managed, through optimal carbon-to-nitrogen ratios, moisture control, and oxygen availability. It destroys pathogens and supports beneficial microbial activity.
Compost that reaches 131–170°F consistently meets safety standards and enhances soil health. The end product typically contains slow-release nutrients (NPK) and can be sold for $15–$40 per ton, turning waste into a profitable input.
5. Lower Operational Costs with Waste Reduction Strategy
Beyond composting, strategic waste reduction focuses on minimizing the volume of manure and streamlining storage, handling, and transportation. This includes separating solids from liquids, adopting efficient manure drying methods, or implementing belt or scraper systems to facilitate efficient waste management.
These practices reduce hauling frequency, lower disposal costs, and free up storage space in helping feedlots maintain cleaner environments, cut labor demands, and improve compliance.
6. Strategic Nutrient Management Planning for Sustainable Manure Use
A well-designed nutrient management plan turns manure from a liability into a strategic asset. By aligning manure application with crop nutrient needs and environmental regulations, operators can reduce costs, improve soil health, and protect water quality.
- Start with Soil Testing: Regular, detailed soil tests help identify nutrient deficiencies or excesses, allowing targeted manure application that boosts efficiency and reduces synthetic fertilizer use.
- Match Nutrients with Crop Demand: Timing is critical—applying manure when crops can absorb nutrients (e.g., during key growth stages) prevents runoff and enhances yield.
- Protect Sensitive Areas: Incorporating buffer zones and setbacks into your plan helps avoid water contamination, meets compliance, and promotes environmental stewardship.
When implemented correctly, nutrient planning not only ensures regulatory compliance but also directly contributes to operational sustainability and profitability.
What Benefits Does Effective Manure Management Deliver?
The benefits of strategic manure management extend far beyond regulatory compliance, creating value across multiple dimensions of feedlot operations.
1. Reduce Operational Costs Through Smarter Manure Management
Manure management reduces waste disposal costs and transforms manure into a revenue-generating asset. Operations that sell processed manure can recoup up to 100% of handling expenses. Cleaner pens improve feed efficiency by 3–8%, resulting in lower per-head feed costs.
Veterinary expenses drop due to fewer respiratory and lameness issues. It also boosts crop yields by recycling nutrients and reduces reliance on commercial fertilizers, fuel, and equipment maintenance due to improved facility cleanliness.
2. Achieve Environmental Compliance and Avoid Regulatory Setbacks
Effective manure management ensures compliance with evolving water and air quality regulations. It prevents surface and groundwater contamination through controlled storage and application. Proper handling also minimizes ammonia emissions, dust, and odors, thereby improving air quality and fostering better community relations.
Digital documentation tools streamline regulatory reporting and audit readiness. Staying compliant not only avoids costly fines but also protects the operation’s public image, helps retain operating permits, and secures eligibility for environmental incentive programs.
3. Improve Animal Health and Overall Productivity
Manure control has a direct impact on animal comfort, reducing respiratory stress, cattle heat stress, and disease risk. Cattle in cleaner environments consume more, gain weight more quickly, and require fewer medical treatments, resulting in lower health costs and improved feed-to-weight ratios.
Cleaner surfaces reduce lameness by up to 40%, improving mobility and performance. Reproductive efficiency also improves due to healthier body conditions and lower stress levels. Collectively, these factors result in greater yield per head and higher overall profitability.
4. Enhance Soil Health and Long-Term Fertility
Manure, when properly treated and applied, enhances soil structure, improves water retention, and stimulates microbial activity. Over time, this reduces dependency on chemical fertilizers, improves crop resilience, and enhances yields. It also promotes carbon sequestration, which is beneficial for both soil vitality and climate initiatives.
5. Strengthen Biosecurity and Disease Control
Clean, well-managed environments lower pathogen loads and reduce the risk of cattle diseases. Reducing manure buildup helps curb the spread of E. coli, Salmonella, and other harmful microbes, creating a safer environment for both animals and workers.
6. Support Sustainable Branding and Market Access
Sustainable manure practices align with consumer and retailer expectations for environmentally responsible production. Operations with documented sustainability practices are more competitive in premium markets and may qualify for grants, certifications, and eco-labeling programs.
How Folio3 Feedlot Software Simplifies Manure Management for Better Results?
Modern feedlot operations require sophisticated information management systems to track, analyze, and optimize manure management activities. Folio3 AgTech feedlot management software provides the tools necessary to transform manure management from a reactive compliance activity into a strategic operational advantage.
Manage Scraping Cycles, Export Loads, and Stockpile Tracking
Folio3 AgTech’s Feedlot Management Software features a Feedyard Maintenance module that enables operators to track and schedule manure management activities efficiently.
From managing scraping cycles and export loads to monitoring stockpile locations, the module ensures all tasks are documented and completed on time. This not only supports better nutrient planning and operational efficiency but also simplifies compliance reporting with structured, audit-ready data.
Improve Pen Cleaning with Cattle Pen Maintenance Logs
Operators can log pen cleaning activities by pen ID, date, and the name of the responsible personnel. This ensures consistent cleaning schedules, supporting better animal health and environmental control while enabling smart crew scheduling.
Track All Waste Streams for Complete Oversight
The waste management tracker monitors deadstock handling, medical waste, and general cleanup activities. Each action is documented with timestamps and disposal methods, offering transparency and aiding continuous improvement.
Proactive Task Management with Alerts and Notifications
Built-in alert systems flag overdue tasks, unresolved issues, and critical maintenance needs. This enables managers to respond quickly, avoid costly delays, and maintain consistent execution across all operations.
Simplify Regulatory Reporting and Compliance
Generate audit-ready reports for DEQ inspections, SOP documentation, and environmental compliance directly from the system. Folio3’s reporting tools save time while ensuring full adherence to regulatory standards.
Optimize Equipment Performance with Maintenance Logs
The software tracks servicing needs for scrapers, loaders, and pumps based on usage hours or service intervals. This supports a preventive maintenance strategy, which minimizes downtime and extends equipment lifespan.
Conclusion
Manure management isn’t just about checking the compliance box anymore, but it’s a real opportunity to reduce costs, improve productivity, and build a more sustainable feedlot operation. When done right, it can turn a liability into a resource that supports soil health, animal well-being, and your bottom line.
The key is finding the right tools tailored to your unique operation. That’s where Folio3 AgTech comes in. Our feedlot management solutions are built to help you streamline manure handling, stay compliant, and unlock long-term value, without the extra stress.
FAQs
How Can Feedyard Maintenance Software Help In Managing Manure?
It tracks scraping, stockpiling, and exports while automating alerts and compliance reports for efficient, regulation-ready operations.
What Are The Key Strategies For Manure Management In Beef Feedlots?
Effective strategies include proper storage, precision application, composting, and nutrient planning tailored to site-specific conditions.
How Does Composting Benefit Beef Feedlots?
Composting reduces manure volume by 40-60%, destroys pathogens, eliminates odors, and creates a marketable product that commands premium prices. The process transforms waste disposal costs into revenue opportunities while reducing transportation and storage requirements.
What Are The Environmental Benefits Of Proper Manure Management?
Proper manure management prevents water contamination, reduces air emissions, improves soil health, and supports sustainable agricultural practices. These benefits enable operators to maintain their social license to operate while complying with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.