Imagine you buy a bag of prepared salad from the supermarket. You eat the salad at home and unintentionally bite into a piece of glass that may have been mixed in with the salad when it was packed at the food processing facility. Thus, you end up with a mouth injury and head straight to the hospital.
Your case is only one of numerous reports of food contamination. It highlights how important food companies are to maintaining food safety and protecting consumers’ health.
In this blog, we will learn the most common types of food contamination and look at how food businesses can use measures to detect and prevent these contaminants before they reach the end consumer.
What is Food Contamination?
Food contamination is the term used to describe hazardous substances or microbes that contaminate food, making it unsuitable for human consumption and threatening public health. It can happen at any point in the production or supply chain, often due to improper handling, storing, or processing of food products.
“Prevention is better than cure.” Avoiding actions that cause contamination is essential; handling food efficiently is the only way. Ensuring food safety is the responsibility of food handlers and providers, and putting quality and cleanliness first may help with half the work. Managers responsible for food safety are essential to this process. They closely monitor every link in the food chain to prevent any physical, chemical, or biological food contamination.
What are the Three Types of Food Contamination?
No matter what type of food business you operate, whether a food packaging company or a restaurant, you must be aware of three types of food contamination. You should take every safety precaution to ensure your food is safe from these contaminants.
The following are three types of food contamination:
Biological Contamination
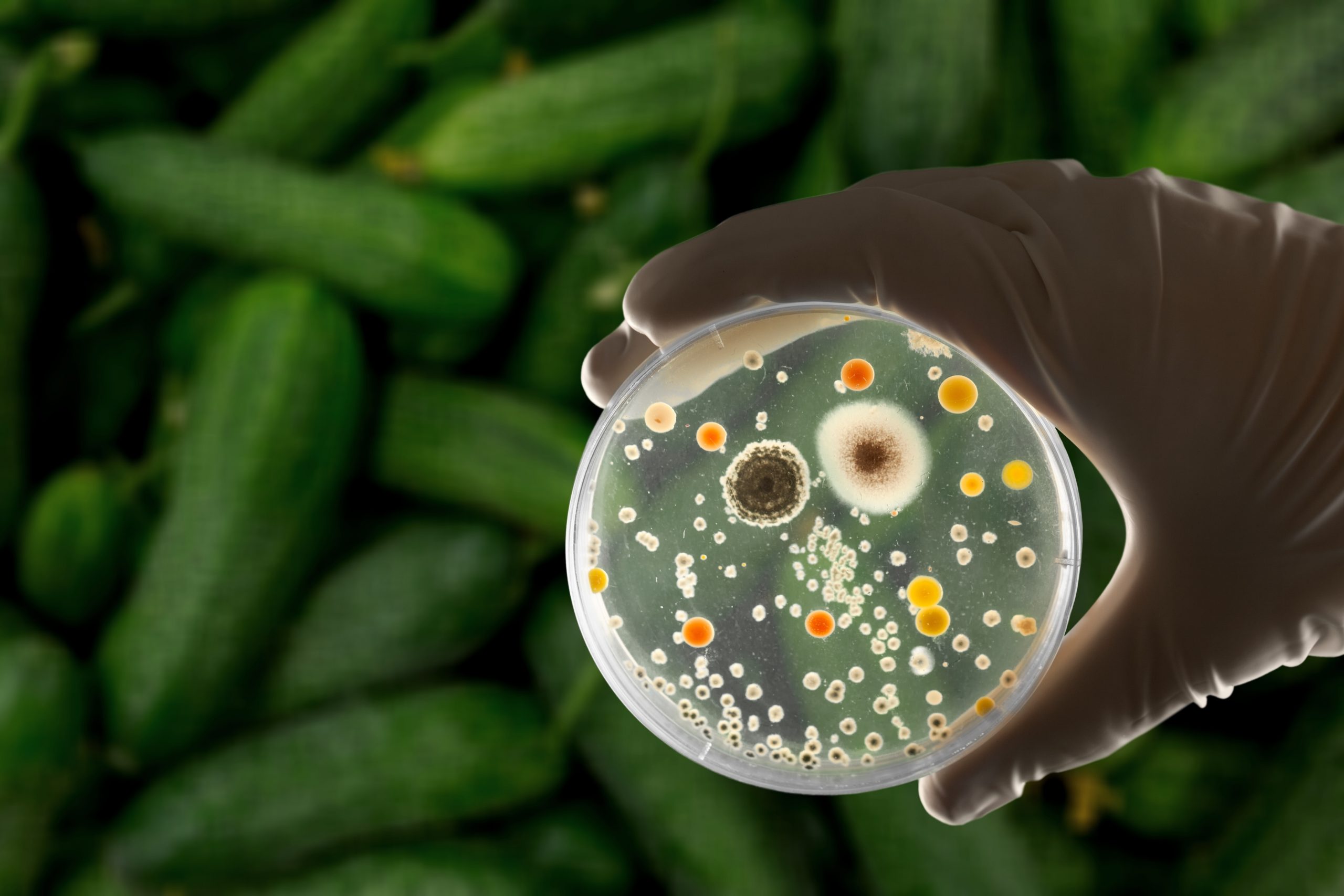
Contamination of food items by other living organisms is known as biological contamination. It is the existence of harmful microorganisms in food, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. Food items are very susceptible to the influence of microorganisms, which need favorable conditions to become active. For instance, food might lose its texture and color and become more acidic and odorous in mild temperatures.
Food with microbial contamination is not edible, and the effects of such food can be severe. The probability of microbial contamination is very high in food products that are open to environmental contamination, such as soil, water, and animals in the case of animal-origin food. However, microbial contamination may be avoided before food is consumed by adequately preparing and boiling the components.
Physical Contamination
When any foreign object contaminates food, physical contamination of food occurs. Physical contamination gives physical wounds! It can cause injury to the mouth, throat, and digestive system. In extreme cases, it can lead to internal bleeding, blockages, or perforations of the digestive tract. The presence of physical contaminants can also result in choking or asphyxiation. Not only this, but also it can lead to biological contamination. Even if a fingernail does not hurt the body, it can introduce a hundred germs and bacteria to the food, making it inedible.
The proper inspection makes it easy to prevent physically contaminated food from reaching consumers.
However, some unnoticed contamination can still occur even after all the inspections. That’s where FoodTech comes in, to monitor every food product closely and ensure that they are safe to eat, with 100% reliability.
Chemical Contamination
Chemical contamination happens when food becomes contaminated by natural or artificial chemical substances. Depending on the quantity and kind of chemicals in the food, chemical contamination might impact human health.
Short-term side effects might include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Any point in the food chain where pesticides on agricultural products, utensils coated with non-food grade materials, or food preparation methods using excessive additives or toxins can lead to chemical contamination. It may have a very negative impact on customers’ health.
Primary Reason Behind Food Contamination
Among the three types of food contamination, biological contamination is considered the primary cause of food contamination. Biological agents, such as bacteria, viruses, molds, yeasts, and parasites, primarily cause food contamination. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) speaks in a study that found out that, out of 250 identified foodborne diseases, most are attributed to bacteria, viruses, and parasites. These microorganisms can be naturally present in the environment, which makes the food more prone to them if the necessary measures are not taken. Most of these organisms are mobile and can quickly spread through cross-contamination from one food item to another, making them a significant risk to food safety.
Microbial contaminants can quickly spread through cross-contamination and cannot be detected with the naked eye. It makes it easy for food handlers who need to follow proper food-handling practices to disperse them. On the other hand, physical and chemical contamination is more detectable. And the fact that both physical and chemical contamination leads to biological contamination cannot be ignored. Bacterial contamination can occur rapidly and easily unnoticed until it spoils the food completely. It can quickly spread food to food. Some microorganisms can multiply rapidly, doubling in numbers within minutes under favorable conditions, resulting in a significant rise in contamination within a short period.
It is clear that the top reasons for food contamination are microbial, and they occur when food makers use low-quality ingredients and utensils, follow poor food management and storage conditions, and neglect hygiene and clean food preparation conditions.
Understanding the Various Types of Food Contamination
To better understand what food contamination is? And how the contamination occurs. Let’s take food contamination examples for each type.
Example of Biological Contamination
Salmonella, a bacterium, can contaminate eggs or poultry during processing, handling, or storage. If food handlers neglect precautions, these tainted products can reach consumers. Consumption of Salmonella-contaminated poultry can result in salmonellosis, characterized by symptoms such as fever, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Typically, salmonella symptoms manifest within 12 to 72 hours post-ingestion and may persist for up to a week.
In a similar manner, E. coli can contaminate ground beef during processing, leading to E. coli infection. This infection presents symptoms like stomach cramps, diarrhea (sometimes bloody), and vomiting.
Examples of Physical Contamination
Examples of physical food contamination encompass various forms such as glass, metal, hair, or plastic. For instance, a piece of glass might inadvertently mix into a salad from a shattered container, a stray hair could drop into soup during preparation, and metal shavings could inadvertently end up in canned food during the manufacturing process.
The consumption of a salad containing a fragment of broken glass can result in cuts or broken teeth, causing pain and discomfort. At times, the contamination can be severe enough to lead to internal injuries. Although physical contaminants are usually visible and identifiable, they may go unnoticed due to inadequate food handling and hygiene practices. For instance, the presence of hair strands in food often signifies poor hygiene standards among chefs. While this type of physical contamination may not necessarily harm consumers physically, it can introduce biological contamination through the presence of germs and bacteria.
Examples of Chemical Contamination
If a pesticide is not used correctly, it can contaminate the food (fruit or vegetable) intended to protect. If not washed correctly, the pesticide residue can remain on the product and spoil it. Even if it gets cleaned, but the cleaning agent is not rinsed off properly, it can still contaminate the food chemically.
Another example of chemical contamination is the presence of toxic metals such as mercury in fish due to biomagnification. These food contaminations can easily be avoided with proper food management and handling.
How Does Food Contamination Impact Consumers and the Economy?
In low- and middle-income countries, the annual production loss due to foodborne illness is anticipated to be $95.2 billion. According to 2019 World Bank research, the yearly cost of treating foodborne infections is expected to be US$ 15 billion. Long-term diseases caused by food contamination decrease productivity and increase the economic burden on both individual and national levels due to the increased healthcare costs.
Food safety assists national economies, tourism, trade, nutrition, food security, and long-term development. For instance, if contamination occurs in a food processing plant responsible for exporting products to other countries, it can lead to a significant loss of revenue and a decline in the economy’s growth rate.
People are less likely to visit countries with low-quality food manufacturing and processing standards. It is evident that directly or indirectly, food contamination impacts the economy on the national level as much as it affects consumers individually.
As contaminated food is unfit for consumption, it gets disposed of to prevent foodborne illnesses. However, this practice goes against sustainability objectives, making it difficult to ensure safe food availability. Contamination can disrupt the entire food chain, decreasing the food supply and impacting food security. The economic impact of food contamination extends beyond the food industry and can slow down community growth.
These problems place additional responsibilities on food producers and handlers to maintain food safety. Because of the speed and breadth of product distribution, local issues can swiftly escalate into international crises. To prevent this, a functional food safety management system is necessary. FoodTech can provide an all-in-one solution from digital monitoring forms, unlimited cloud storage, and real-time dashboards to alerts and notifications.
How to Detect Contamination of Food?
Food companies have access to a variety of methods for identifying various forms of food contamination.
For example, biological pollutants like bacteria, viruses, and parasites can be found using microbiological testing techniques. Biological contaminants may be identified with the use of mass spectrometry. In addition, another cutting-edge technique that aids in the identification of bacteria in a food sample is LIBS (Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy).
Mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, and chromatography are examples of analytical techniques used to identify chemical pollutants. Applying methods like atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) to identify and measure metal ions while using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separates the components in food samples.
Physical contaminants, including plastic, metal, or glass, are usually found by hand sorting, visual examination, or the use of specialist machinery like X-ray machines and metal detectors. These instruments use composition or density to identify foreign elements.
Furthermore, nanosensors that make use of nanotechnology can assist in identifying different kinds of food contamination. These chemical or biosensor sensors provide quick, accurate, and accessible contamination detection for a variety of substances, such as allergies and mycotoxins.
Wireless technology integration with nanosensors allows for real-time results transmission, improving food safety management efficiency and cutting costs.
How to Prevent Food Contamination?
Now that we know the different types of food contamination, we must also know that implementing proper food safety measures to prevent these contaminants is crucial to protecting public health, ensuring food security, and maintaining a sustainable food system. Preventing food contamination involves implementing food safety practices at every step of food production and preparation, from the farm to the table.
Controlling Food Contamination with FoodTech
Folio3 FoodTech is a food safety management system used by food companies to ensure that their products are safe and satisfy quality standards. It’s a tool for managing food safety that ensures that all the food made meets quality standards, indicating that it’s safe to eat.
There are a lot of benefits of using a food safety software. For instance, FoodTech relieves stress by making your job more efficient and information accessible to update, allowing you to focus on other elements of your food service business.
With EcoDocs, you can run more smoothly, avoid more issues, and even identify and rectify essential issues in real-time, entirely paperless, preventing problems down the road and saving time and money.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have learned that biological, physical, and chemical contaminants are the three primary types of food contamination. While physical contaminants are much easier to detect, biological contamination presents a significant challenge due to its invisibility. The economic repercussions of food contamination are also quite substantial and affect productivity and healthcare costs.
However, several measures can be taken to prevent contamination in food, such as implementing food safety practices and using software solutions to ensure compliance. It can help mitigate food safety risks and provide safe production and consumption.
FAQs
What Types of Contamination Can Occur in Food?
The four types of food contamination include:
- Physical Contamination
- Chemical Contamination
- Biological Contamination
- Allergic Contamination
What are the five food contaminants?
The five most common food contaminants are:
- Bacteria: Such as Listeria, Salmonella and E. coli.
- Viruses: Such as Norovirus and Hepatitis A.
- Parasites: Such as Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium
- Chemicals: Pesticides, heavy metals, and food additives.
Allergens: Allergens such as peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, and soy can cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
What are examples of contaminated foods?
Examples of contaminated foods include
- raw meat
- unpasteurized milk and dairy products
- undercooked eggs
- contaminated produce such as lettuce
What are 5 ways food can be contaminated?
Common ways that can contaminate food include
- low hygiene conditions
- low-quality ingredients and utensils
- poor food management codes of conduct
- inadequate food storage
What is an Example of Physical Contamination?
Common examples of physical contamination include broken glass, pieces of plastic, metal shavings, wood fragments, insects, human/animal hair, stones, and rocks.
Metal Shavings are Which Type of Contaminant?
Metal shavings are commonly classified as physical contaminants. Small pieces of metal can enter food during manufacturing.